Emotet
Threat Scorecard
EnigmaSoft Threat Scorecard
EnigmaSoft Threat Scorecards are assessment reports for different malware threats which have been collected and analyzed by our research team. EnigmaSoft Threat Scorecards evaluate and rank threats using several metrics including real-world and potential risk factors, trends, frequency, prevalence, and persistence. EnigmaSoft Threat Scorecards are updated regularly based on our research data and metrics and are useful for a wide range of computer users, from end users seeking solutions to remove malware from their systems to security experts analyzing threats.
EnigmaSoft Threat Scorecards display a variety of useful information, including:
Popularity Rank: The ranking of a particular threat in EnigmaSoft’s Threat Database.
Severity Level: The determined severity level of an object, represented numerically, based on our risk modeling process and research, as explained in our Threat Assessment Criteria.
Infected Computers: The number of confirmed and suspected cases of a particular threat detected on infected computers as reported by SpyHunter.
See also Threat Assessment Criteria.
| Threat Level: | 80 % (High) |
| Infected Computers: | 4,934 |
| First Seen: | June 28, 2014 |
| Last Seen: | October 24, 2025 |
| OS(es) Affected: | Windows |
 Emotet started as a banking trojan at some point in 2014 but has turned into so much more. Nowadays, it has become one of the most dangerous botnets and malware droppers-for-hire in the world. To fully monetize the attacks, Emotet often drops new banking trojans, email harvesters, self-propagation mechanisms, information stealers, and even ransomware.
Emotet started as a banking trojan at some point in 2014 but has turned into so much more. Nowadays, it has become one of the most dangerous botnets and malware droppers-for-hire in the world. To fully monetize the attacks, Emotet often drops new banking trojans, email harvesters, self-propagation mechanisms, information stealers, and even ransomware.
Security researchers noted that the threat actors behind Emotet took a summer vacation, starting in June 2019, in which even the command and control (C2) activities came to a halt. As the summer months began to come to their conclusion, however, security researchers began to see an increase in the activity of Emotet's C2 infrastructure. As of September 16, 2019, Emotet is already in full gear with a reinvigorated spam campaign, relying on social engineering. Moreover, experts have found cases of Emotet actively spreading the TrickBot Trojan horse, which is used to steal sensitive information that could be leveraged by Emotet hackers for finding out if the victim is a viable target. TrickBot, along with Emotet, is also an agent that has lead to the propagation and targeting of Ryuk ransomware, an aggressive form of malware that encrypts files on an infected system while making demands to the computer user to pay a ransom to have the files restored.
Table of Contents
Emotet Takes a Hiatus Again in 2020
The cybercriminals running Emotet took some time off in 2020 as well. This time the hiatus lasted 5 months from March to July. Emotet activity resumed in August and by early September Emotet was back in full force. So much so that CERTs (computer emergency response team) from three countries had to issue specific warnings about Emotet attacks. The targeted countries were New Zealand, Japan and France. The first two saw significant increases in infections and attacks with CERT Japan reporting that detections tripled in a week. In France, the activity was more moderate but enough to warrant a reaction from the CERT. A couple of weeks later, Microsoft also issued a warning about Emotet and so did agencies from Italy and the Netherlands.
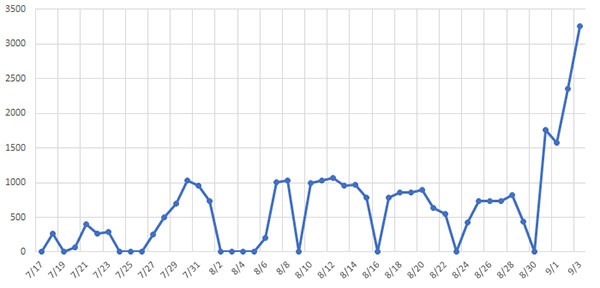
Emotet Trojan infection increase rates chart - source: JPCERT.or.jp
Emotet joined the password-protected attachment bandwagon with a campaign starting Friday. The campaign slowed down over the weekend (typical of Emotet) but was back today in even larger volumes of emails in English, as well as in some European languages. pic.twitter.com/POppQ51uMX
— Microsoft Security Intelligence (@MsftSecIntel) September 22, 2020
Emotet Targets Computer Users Through Enticing Spam Email Campaigns
One of the most ingenious and menacing ways through which Emotet infected victims was through stolen email content. The malware would swipe a victim's inbox and copy existing conversations, which it will then use in its own emails. Emotet will quote the bodies of real messages in a "reply" to a victim's unread email, in a bid to trick them into opening a malware-laced attachment, usually in the guise of a Microsoft Word document.
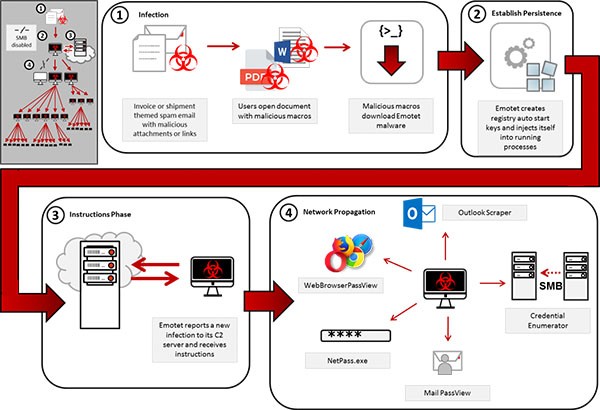
Emotet Trojan horse infection process paths - source: US-CERT.cisa.gov
It doesn't take a lot of imagination to see how someone expecting a reply to an ongoing conversation could be fooled in this manner. Furthermore, by mimicking existing email conversations, including genuine email contents and Subject headers, the messages become much more randomized and challenging to filter by anti-spam systems.
What's interesting is that Emotet doesn't use the email from which it stole content to send it to a potential victim. Instead, it sends the lifted conversation to another bot in the network, which then sends the email from an entirely different location, using a completely separate outbound SMTP server.
According to security researchers, Emotet used stolen email conversations in about 8.5 percent of attack messages before its summer hiatus. Since the vacation season has come to a close, however, this tactic has become more prominent, accounting for almost a quarter of all of Emotet's outbound email traffic.
Political Messaging
Up until 2020, Emotet's operators had stayed away from any overtly political themes. However, with the presidential elections booming on the horizon, the presidential campaigns became too hot to ignore. In August 2020 Emotet launched a phishing campaign leveraging the attention garnered by the president of the US. The cybercriminals sent out emails with the subject: "Fwd:Breaking: President. Trump suspends funding to WHO." The email body the was actually taken verbatim from a legitimate PAC mailer, however, it contained the usual malicious Word document. This campaign shouldn't be misconstrued as an act of taking a political position as soon after that Emotet launched another phishing campaign, this time targeting the democrats. The phishing emails in that campaign had this as a subject line: "Team Blue Take Action." The body of the emails was taken from the website of the Democratic National Committee which is a legitimate organization. While those two phishing campaigns don't reveal the political affiliation of Emotet's operators (if any), they do match the cybercriminals modus operandi of going for whatever theme they deem popular enough.
Cybercrooks Leverage Emotet to Steal Personal Data
The tools at the disposal of cybercrooks looking to steal personal information from computers is virtually endless. It just so happens that Emotet is a type of malware threat that is highly effective at leveraging in a way to launch mass spam email campaigns that spreads malware designed to steal data from an unsuspecting computer user. The way in which Emotet works is to open up a backdoor for other high-risk computer threats, such as the Dridex trojan horse, which is specifically designed to steal data from a computer user using aggressive phishing techniques.
This Week in Malware Video: Episode 1 covering the triple threat campaign of Emotet, Trickbot & Ryuk Ransomware are stealing and ransoming data.
When used by the right type of hacker or cybercrook, Emotet may be used in a way to infiltrate a computer to load and install multiple malware threats. Even so, the additionally installed threats may be more dangerous where they may connect to command and control (C&C) servers to download instructions to carry out on the infected system.
The Effects of Emotet Should Never Be Taken Lightly
In any case of a malware threat as far-reaching as Emotet, computer users should take necessary precautions to prevent an attack from such. On the flip side, those who have been attacked by Emotet will want to find the necessary resource to safely detect and eliminate the threat. If one allows Emotet to run on a computer for a long period of time, the risk of having data pilfered exponentially increases.
Computer users who may delay in eliminating Emotet or taking the proper precautions will put their personal data stored on their PC at risk, which could lead to serious issues like identity theft. Moreover, Emotet is a difficult threat to detect, which is a process that is primarily done by an updated antimalware resource or application.
At all times, computer users should utilize caution when opening emails with attachments, specifically ones that contain attachments in the form of Microsoft Word documents, which is known to be a method that Emotet uses to spread malware.
The Return of Emotet
At one point in 2019, Emotet's command and control servers where shuttered leaving systems infected by the threat free from being under the control of the perpetrators behind Emotet. However, not too soon after the shut-down of the C&C servers, Emotet came back from the dead where hackers not only gained control of Emotet, but they are using legitimate websites to spread the threat via spam campaigns by first hacking the sites.
Emotet’s developers have reportedly targeted about 66,000 email addresses for over 30,000 domain names, many of those domains belonging to legitimate sites that were hacked. Some of the legitimate sites attacked by the creators of Emotet are the following:
- biyunhui[.]com
- broadpeakdefense[.]com
- charosjewellery[.]co.uk
- customernoble[.]com
- holyurbanhotel[.]com
- keikomimura[.]com
- lecairtravels[.]com
- mutlukadinlarakademisi[.]com
- nautcoins[.]com
- taxolabs[.]com
- think1[.]com
Fundamentally, we will see an increase in malware infections as sure as time progresses. As researchers from Cisco Talos noted: "When a threat group goes silent, it's unlikely they'll be gone forever," elaborating: "Rather, this opens up the opportunity for a threat group to return with new IOCs, tactics, techniques, and procedures or new malware variants that can avoid existing detection."
SpyHunter Detects & Remove Emotet
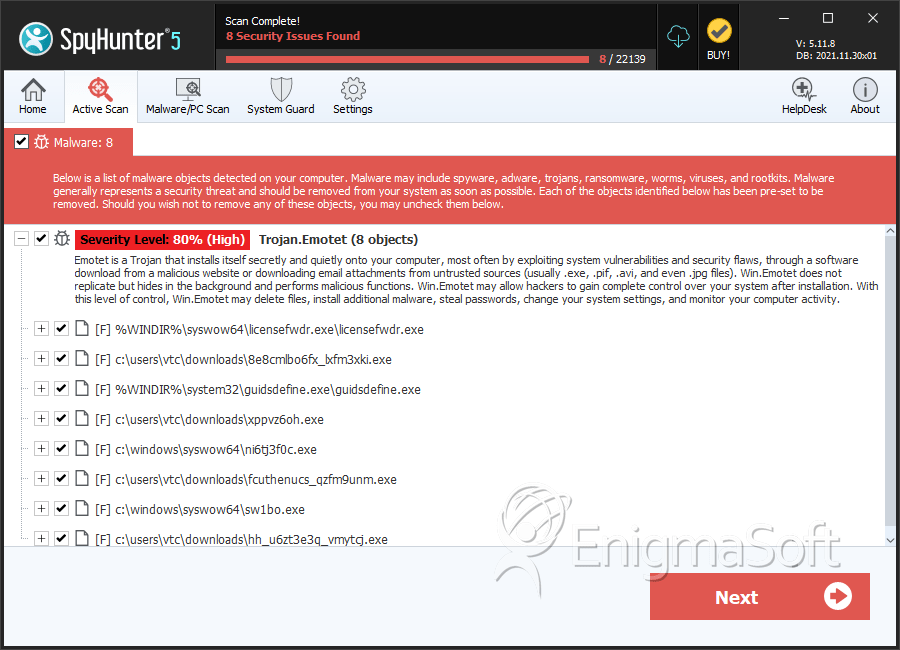
File System Details
| # | File Name | MD5 |
Detections
Detections: The number of confirmed and suspected cases of a particular threat detected on
infected computers as reported by SpyHunter.
|
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | licensefwdr.exe | 3391006372b212ba0be34bf9cc47bb15 | 62 |
| 2. | 8e8cmlbo6fx_lxfm3xki.exe | 0d87835af614586f70e39e2dfdba1953 | 41 |
| 3. | guidsdefine.exe | 8af726850d90d8897096429c8f677fb9 | 34 |
| 4. | ni6tj3f0c.exe | 865eba9b4ee8e93f500232eae85899f9 | 14 |
| 5. | sw1bo.exe | 6957fc973e45d6362c9508297840332c | 14 |
| 6. | fcuthenucs_qzfm9unm.exe | fc620fb26d06a3f15e97fa438e47b4e3 | 13 |
| 7. | hh_u6zt3e3q_vmytcj.exe | 0c12b6e792d5e395f1d0e8e00f2a906b | 9 |
| 8. | 8lqwejk6.exe | 9ab8c51587e3a46950576c545d917e5f | 8 |
| 9. | guidsripple.exe | 954d6e95ef173331841a54b2bacbcd28 | 8 |
| 10. | z7w2_qj.exe | 59dec5b309f882bd3b7b7f4db9de8810 | 7 |
| 11. | file.exe | 110c1f03f6cea56bbc5aea62e9705d24 | 7 |
| 12. | ripplepolic.exe | d3fe0e7a94cf8a04435ecd85d1a85227 | 7 |
| 13. | ↇↂↂↂ自転車выпLXXX;ↇↂↂↂ;ЧыПبايسکل.exe | 9d7b1ffdd0d6e8e43032b16dabcb52b4 | 7 |
| 14. | BA1E.tmp | b25ec6e225cf6247dcb3810470ae86b7 | 6 |
| 15. | 211.exe | 831bbafd3a5596994e3e5407e86a6ab0 | 6 |
| 16. | s9nevcf77pvpbcahes.exe | 9f6d496199d712df75fea0d4f65a774d | 6 |
| 17. | სკუმბრია.exe | 35c973fee6e0f6fd1c9486d25d041c83 | 5 |
| 18. | fu_nid7mlnsu.exe | fecc9b87f6adde022e2e7540469d9668 | 4 |
| 19. | td5g1cst.exe | d42dbba27dc711e5b4a3f4bf83967049 | 4 |
| 20. | cvedvfdyaj.exe | e60048bfaab06dcab844454c33ad5491 | 4 |
| 21. | aizz7dugmz_ddw.exe | 149f8faf3bb1c3cbd1207c133715a480 | 2 |
| 22. | h7kg8jsthbc.exe | c6c70da245a63f7ae7052ebac3fb76c6 | 2 |
| 23. | troj_generic_ec086af0e56b97ea6b427f02f90def0897bb0fe578eed1d48bf33049e4c9d439.exe | 536d98819ef25d5452ef802d4541bb46 | 1 |
| 24. | bc117e6ae77ef72ad0131990943d7a8b3570f0eb9fbe9a7a41e7e43711e5f763.crdownload | 83e70065bf06162895e73ce43f4fdb19 | 1 |
| 25. | eb7f8d53312376570fbd1385b45d1ff3fab6faadfba6c3a3a6c9d30c5e31bb4d.crdownload | 1f4a1df52756bd6ea855b47f039836ee | 1 |
| 26. | 1be6989616522d6ae9b3c301e5f51f0ac0313dfc8497958c616a307cd09657fc.crdownload | 991bd07e70c478affb777a3728942591 | 1 |
| 27. | aba5311be7e0dfbfefdd1f545a701b4e81c9ad8790af6f58f827e6b54f3454e5.crdownload | a4d00e6314149af840bbbf7a70bf1170 | 1 |
| 28. | a9a90901ee38e8a232e253f00b9fc9c0f0f58620ef6b7692e6dc7342a7317c1d.crdownload | 6f68c6733db5e38ba4cd82d12e683696 | 1 |
| 29. | C:\Windows\11987416.exe | ||
| 30. | C:\Windows\System32\46615275.exe | ||
| 31. | C:\Windows\System32\shedaudio.exe | ||
| 32. | C:\Windows\SysWOW64\f9jwqSbS.exe | ||
| 33. |
C:\Users\ |
||
| 34. |
C:\Users\ |
