LokiBot
Threat Scorecard
EnigmaSoft Threat Scorecard
EnigmaSoft Threat Scorecards are assessment reports for different malware threats which have been collected and analyzed by our research team. EnigmaSoft Threat Scorecards evaluate and rank threats using several metrics including real-world and potential risk factors, trends, frequency, prevalence, and persistence. EnigmaSoft Threat Scorecards are updated regularly based on our research data and metrics and are useful for a wide range of computer users, from end users seeking solutions to remove malware from their systems to security experts analyzing threats.
EnigmaSoft Threat Scorecards display a variety of useful information, including:
Ranking: The ranking of a particular threat in EnigmaSoft’s Threat Database.
Severity Level: The determined severity level of an object, represented numerically, based on our risk modeling process and research, as explained in our Threat Assessment Criteria.
Infected Computers: The number of confirmed and suspected cases of a particular threat detected on infected computers as reported by SpyHunter.
See also Threat Assessment Criteria.
| Ranking: | 12,271 |
| Threat Level: | 80 % (High) |
| Infected Computers: | 75 |
| First Seen: | February 24, 2017 |
| Last Seen: | August 22, 2023 |
| OS(es) Affected: | Windows |
LokiBot Image
LokiBot is a threat that is used to collect information from affected computers. LokiBot includes a keylogger component that can be used to collect the victim's passwords and login data and then sends them to an external server, where the criminals can then access the victim's data and online accounts. The main way in which LokiBot is being distributed is through the use of spam email campaigns, which will often use corrupted email attachments to deliver threats like LokiBot to the victims' computers. Once LokiBot is installed, LokiBot is capable of collecting a wide variety of usernames, passwords, and numerous other components, as well as information related to cryptocurrency wallets and other online accounts.
Table of Contents
How LokiBot is Distributed
The most common way in which LokiBot is used to carry out attacks is by exploiting a vulnerability in Windows known as CVE-2017-11882. This is an exploit that was patched by Microsoft recently, but there also are many computer users that have not updated their computers so that they may still be vulnerable to the exploit being used to deliver LokiBot. The method used to deliver LokiBot, which involves an MSI installer, has been used in the past to deliver low-grade threats and Potentially Unwanted Program (PUPs), such as adware and similar threats. However, it seems that this method is being leveraged by criminals to deliver m severe malware like LokiBot.
This Week In Malware Episode 25 Part 1: LokiBot Ransomware Attacks On The Rise Stealing Passwords & Cryptocurrency Wallets
Which is the Best Way to Handle the LokiBot Attacks
Since the most common way in which LokiBot is delivered (as well as many other threats) is via spam email attachments, learning to recognize these tactics and reacting to them appropriately is essential in dealing with attacks like LokiBot and preventing their impact. However, a reliable security program that is fully up-to-date can help prevent LokiBot from being installed. One additional aspect of LokiBot is the fact that this particular campaign is leveraging a very specific vulnerability in Windows. Having the latest security patches can ensure that potential victims are safe from threats like this one.
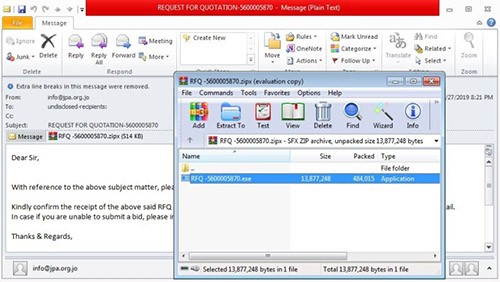
The LokiBot spam campaign from which it is believed that the threat is able to spread, comes as an obfuscated .zipx archive file that unpacks the LokiBot attack. The file comes as an attachement in a spam email as shown in Figure 1 below.
Figure 1. LokiBot obvuscated RFQ -5600005870.zipx file attached to spam email message
A Brief Explanation about the LokiBot Attack Process
The vulnerability that is being used to distribute LokiBot was patched in November 2017. However, this patch did not stop numerous criminals from using it to deliver a wide variety of threats, ranging from ransomware threats to several data collecting Trojans. The version of LokiBot being distributed is a cracked version of this Trojan, meaning that a second group of criminals has collected this threat from its original creators. LokiBot is capable of collecting login credentials, data from the infected computes, cryptocurrency wallet login credentials, and track keystrokes and other actions executed on the infected computers. There are several components involved in the LokiBot attack, and they are very heavily obfuscated, meaning that it is very difficult for PC security researchers to study their contents or determine with any degree of certainty the LokiBot's code or some essential aspects of the attack.
Preventing LokiBot Attacks
Since LokiBot is commonly delivered using phishing email messages, implementing security measures involved with this content kind in small businesses and organizations targeted in these attacks can help mitigate their impact. Learning to recognize these tactics is often about learning to understand the context and see warning signs that may be present in an email message received on an affected computer. Grammar error and misspelled content is often a cue for computer users to realize that the spam email message is not legitimate, although many of these can be crafted to be highly convincing. However, it is essential to use strong security software to protect your computer from attacks, and a reliable security product that is updated, which will stop threats like LokiBot.
SpyHunter Detects & Remove LokiBot
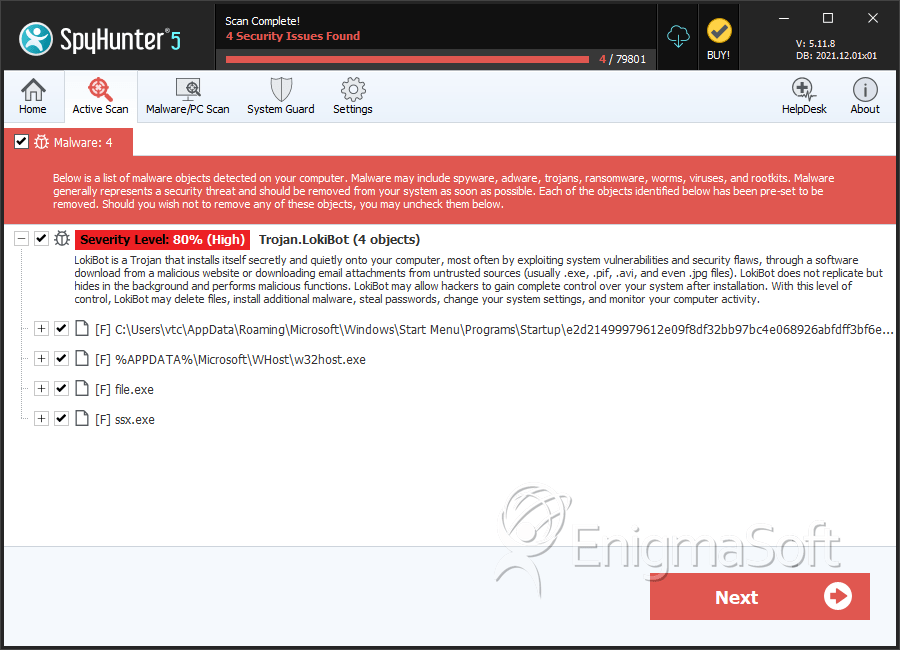
LokiBot Screenshots
File System Details
| # | File Name | MD5 |
Detections
Detections: The number of confirmed and suspected cases of a particular threat detected on
infected computers as reported by SpyHunter.
|
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | w32host.exe | 979b0c6904dfc8ee329705e93f804fc7 | 8 |
| 2. | w32host.exe | f62ae3a83ae40c3503ea193581a82b78 | 5 |
| 3. | e2d21499979612e09f8df32bb97bc4e068926abfdff3bf6e3d451012dabe502d.exe | e07601974ced5b715dfde8e880f0e096 | 4 |
| 4. | w32host.exe | bde54939438664911981d525b12329a7 | 3 |
| 5. | w32host.exe | bd030f64e2219b2a4e8dea41126c8e10 | 3 |
| 6. | file.exe | 91072ab67693d55655781c1ac624e04a | 2 |
| 7. | file.exe | 90cf399b337479372f89f9ac52ef4c73 | 1 |
| 8. | file.exe | a91d75970c089ccd042d477982a9a5be | 1 |
| 9. | RFQ -5600005870.zipx | ||
| 10. | RFQ -5600005870.exe | ||
| 11. | file.exe | 6c53237e57f4e4741d94ee4516850ea7 | 0 |
| 12. | file.exe | fcaaa897743d219dd068d1b5daf7a84b | 0 |
| 13. | file.exe | 2baa56f364907b6687f4a6d392d27a8f | 0 |
| 14. | file.exe | 735d27cb2e3b2460ff76b0f302a758ac | 0 |
| 15. | file.exe | ea305af3668d63046659711057c09ff7 | 0 |
| 16. | file.exe | 475c9739fe565f310c6dcc630f4c5185 | 0 |
| 17. | file.exe | 138c78c4d34cf88415f14d98d1d51a81 | 0 |
| 18. | ssx.exe | f4f7713fec294c7344655c8ddded266b | 0 |
| 19. | file.exe | b193a06dda2b064b6aeb9efb7b4fc4a2 | 0 |
| 20. | file.exe | ac6829c09d6e1ff82721d99f219b6ce2 | 0 |