Google Redirect Virus
Threat Scorecard
EnigmaSoft Threat Scorecard
EnigmaSoft Threat Scorecards are assessment reports for different malware threats which have been collected and analyzed by our research team. EnigmaSoft Threat Scorecards evaluate and rank threats using several metrics including real-world and potential risk factors, trends, frequency, prevalence, and persistence. EnigmaSoft Threat Scorecards are updated regularly based on our research data and metrics and are useful for a wide range of computer users, from end users seeking solutions to remove malware from their systems to security experts analyzing threats.
EnigmaSoft Threat Scorecards display a variety of useful information, including:
Ranking: The ranking of a particular threat in EnigmaSoft’s Threat Database.
Severity Level: The determined severity level of an object, represented numerically, based on our risk modeling process and research, as explained in our Threat Assessment Criteria.
Infected Computers: The number of confirmed and suspected cases of a particular threat detected on infected computers as reported by SpyHunter.
See also Threat Assessment Criteria.
| Threat Level: | 80 % (High) |
| Infected Computers: | 146 |
| First Seen: | September 20, 2011 |
| Last Seen: | May 26, 2022 |
| OS(es) Affected: | Windows |
 The Google Redirect Virus has been around for quite some time and is known by many aliases, although, the primary behavior remains constant. Basically, the Google Redirect Virus plays tricks on the minds of PC users who desire Google web searches by randomly redirecting them to malicious web pages or search engines.
The Google Redirect Virus has been around for quite some time and is known by many aliases, although, the primary behavior remains constant. Basically, the Google Redirect Virus plays tricks on the minds of PC users who desire Google web searches by randomly redirecting them to malicious web pages or search engines.
Table of Contents
The Google Redirect Virus Makes Online Searches Ineffective and Dangerous
The Google Redirect Virus (GRV) has been frustrating Internet users for several years now, yet it looks like there is still no effective method for avoiding the infection. In fact, it has even become one of the most severe cybersecurity issues of our time due to the vast popularity of the Google search engine that allows attackers to reach a large number of potential victims. The malware affects Windows, MacOS, and Linux operating systems, while recently Google Redirect Virus versions for mobile devices have surfaced as well.
Profound research shows that there is not just one particular threat called Google Redirect Virus, the name rather encompasses a series of infections and issues affecting most popular browsers with the common result of redirecting the user to malicious web pages through fake search results. The Google Redirect Virus malware is also known as "Chrome Redirect Virus," "the Google Virus," "Yahoo Redirect Virus," and "Bing Redirect Virus." Newer versions have also been identified, and they are known as "Happilli Redirect Virus" and "Nginx Redirect virus."
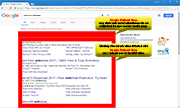
The most obvious symptom of a Google Redirect Virus-type of infection is that all Google searches of a user get redirected to some unknown or shady domains, or to pages of other search engines that could have malicious content. Users having the Google Redirect Virus on their computers will experience the redirecting to unrelated or obnoxious websites when they click on any of the results from their Google search, regardless of which browser they use. Thus, the main functionalities of the Google Redirect Virus have not changed over the years and through the different versions, as well as the intentions of its authors whose main goal is to make money by boosting artificially the visits to their own web pages and the views of the advertisements displayed on them.
All of the locations to which the threat redirects its victims are dangerous since they force the user to purchase malicious software, or may contain scripts that directly install malware or PUPs on the user's device. A clear sign that a PC has been infected with the Google Redirect Virus is that the user gets redirected multiple times from links that are certainly legit, like ebay.com or Facebook. Redirecting programs like the Google Redirect Virus also collect information on users' browsing habits and common search terms, apart from injecting unwanted ads within the search results.
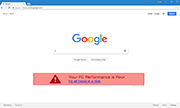
The Google Redirect Virus Disrupts the Overall Performance of Your PC
Google Redirect Virus will not only hijack your browser but also your entire system will be severely impaired so that you might experience some of the following symptoms:
- Unexpected requests for reactivation of drivers
- Applications not running properly
- A changed homepage of your default browser
- Misfunctioning hardware components or drivers
- System freezing or slowing down
- New icons being added to or icons missing from your desktop
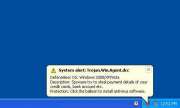
Another possible side effect is the user being assaulted with advertisements, pop-up windows or security alerts. The sudden appearance of unsolicited anti-virus scans that run out of nowhere and warn the user of some non-existing malware threat being detected on his or her PC is also in store for systems infected with a Google Redirect Virus. This last trick is the typical behavior of a rogue security program that attempts to lure the user into purchasing some fake AV software and, respectively, providing their credit card data.
At first sight, the Google virus can be classified as a browser hijacker since it changes the infected browser's settings and causes an overall sluggish and ineffective surfing on the Internet. More recent research shows, however, that this malware can cause more severe damage to infected computers than just the redirecting issues and the annoying ads.
Not a Virus, But a Rootkit
Though its name, a Google Redirect Virus is actually not a virus but a Trojan with rootkit capabilities. The discovery has been made a while ago after the researchers have detected a new malicious program associated with the Google Redirect Virus - it is known as Backdoor.Tidserv. Since then, it is believed that the Google Redirect Virus is a version of the TDSS rootkit which puts itself on the top of a system driver where it cannot be detected and removed. Therefore, any form of the Google Redirect Virus executes malicious commands and employs sophisticated programming techniques to hide its files from anti-virus software radars, making the infection very dangerous, hard to detect, and particularly hard to remove.
As a rootkit-type of malware, Google Redirect Virus is capable of gaining privileged access to the infected computer. Then, it executes redirect scripts into the results of a regular Google search so that the user is redirected to third-party websites when clicking on the search results. A characteristic feature of rootkits is that they use the lower layers of the operating system, like the API function redirection, which makes them really hard to detect. Rootkits can also make the infected system hide from the user existing files and running processes while at the same time displaying non-existent things. A further capability is to download additional threats, like Trojans for example.
Rootkits are extremely hard to remove as well as they integrate themselves into the heart of the operating system. The Google Redirect Virus alters the Master Boot Record (MBR) and makes its own partition on it so that a special anti-rootkit technique is necessary to find the location and this is only possible when the operating system is not running. In addition to that, the malware modifies the main Windows files to receive and execute commands from the attackers while at the same time these files do not look affected since they keep working as normal. Complete removal of the Google Redirect Virus is usually not possible without a professional removal tool.
The Google Redirect Virus Sneaks into PCs Through Many Different Channels
Google Redirect Virus may come bundled within legitimate freeware, shareware, a codec needed to view a movie or any other application that a user deliberately installs without knowing that the package includes hazardous add-ons as well. Plug-ins are another possible means of distribution of the malware, however, the favorite way of rootkits to spread is through Trojan horses. Trojans typically land on a PC when the user opens a malicious email attachment or visits compromised Internet pages. All of these distribution channels exploit users' ignorance of Internet security consisting of blindly installing files and programs without knowing their origin.
Indulging in any of the following activities can explain how a user's PC has become infected with the Google Redirect Virus:
- Clicking on suspicious links and visiting untrusted websites on the Internet
- Opening email attachments from unknown senders or clicking on links embedded into such emails
- Downloading freeware, shareware, or some sort of hacked software or pirated music and movies from dubious sources or networks
- Visiting websites that are notorious for containing dangerous and malicious content, like gambling, gaming or adult web pages
- Not installing a reputable anti-malware application on the computer, or having one with an expired license and an obsolete definitions base
Technical Details of the Google Redirect Virus
Since the Google Redirect Virus is a rootkit, it has the ability to stay hidden within the hard disk of the infected machine for extended periods of time, from where it monitors the user's online behavior and Internet browsing habits. At the same time, the virus does not give any recognizable signs of its presence. In order to identify a Google Redirect Virus on a computer, the user should look for the following processes, which researchers believe to be associated with the malware:
Xzagua.exe
Dmgsh.exe
Xwo.exe
C:\WINDOWS\Xzagua.exe
Xwk.exe
GVR's malicious traces can also be found in the registry as the following registry keys:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\UACd.sys
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\4DW4R3
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\_VOIDd.sys
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\_VOID
DDLs and other files which are known to be related to the malware are:
C:\WINDOWS\system32\UAC.dll
C:\WINDOWS\SYSTEM32\4DW4R3c.dll
C:\WINDOWS\system32\_VOID.dll
C:\Documents and Settings\All Users\Application Data\_VOIDmainqt.dll
C:\WINDOWS\SYSTEM32\4DW4R3.dll
C:\WINDOWS\system32\uacinit.dll
C:\Windows\System32\wdmaud.sys
TDSSserv.sys
C:\WINDOWS\_VOID\
C:\WINDOWS\system32\uactmp.db
C:\WINDOWS\_VOID\_VOIDd.sys
C:\WINDOWS\system32\UAC.db
C:\WINDOWS\system32\_VOID.dat
C:\WINDOWS\system32\drivers\_VOID.sys
C:\WINDOWS\system32\drivers\UAC.sys
C:\WINDOWS\SYSTEM32\DRIVERS\4DW4R3.sys
C:\WINDOWS\SYSTEM32\4DW4R3sv.dat
C:\WINDOWS\SYSTEM32\DRIVERS\4DW4R3.sys
C:\WINDOWS\Temp\_VOIDtmp
%Temp%\UAC.tmp
C:\WINDOWS\system32\UAC.dat
%Temp%\_VOID.tmp
C:\WINDOWS\Temp\UAC.tmp
Below is a general outline of what actions the Google Redirect Virus performs on an infected PC:
Modifies the system registry so that the malware's executable runs at every boot. The malware picks the name of that malicious file at random, and it is different each time so that it cannot be recognized by cybersecurity researchers
Drops a .TMP file in the temporary folder. This file is also randomly named and, later on, it installs other malicious components.
The .TMP file registers itself as a legitimate service in order to bypass the firewall and to avoid AV scanning engines. It achieves that by copying a legitimate .dll file and infusing it with its own script, forcing thus the affected file to load the malicious .TMP file.
The malware then exploits vulnerabilities in Microsoft Windows DLL listing by adding the 'modified' .dll file and having it loaded into the memory along with the other legitimate files.
Once loaded, the malicious .TMP file creates another randomly named file in the PC's 'driver' folder, usually a file with the .sys extension. This random file is the component that conceals all of the malware's malicious files and codes from the user as well as from malware detection tools.
Once the random .sys file is deployed, it drops a .dll file in the system folder and this file is then injected into the SVCHOST executable which, in turn, downloads more malicious components from the hackers' servers. It is these configuration files that help the attackers do the following:
- Prevent programs or applications from running, especially such that threaten the malware's processes
- Spoof email accounts and spam persons on the victim's contact list
- Display or trigger pop-up windows and ads
- Perform HTTP transfers (i.e., to send or receive new transmissions)
- Order DNS attacks
- Download other malicious programs such as:
- Trojan keylogger which can steal vital data out of the cache or directly off web-based forms
- Trojan backdoor which can exploit remote assistance tools to secretly make use of the infected PC
- Trojan hijacker which can change the computer's host files and redirect web searches to malicious or unwanted websites
- Trojan dropper which can drop more malicious components or programs to the PC
Websites Associated with Google Redirect Virus
Some of the suspicious web pages that Google Redirect Virus is known to link to include questionable search engines (like search.babylon.com), adult websites (like livejasmin.com), and ad-supporting services (like adf.ly). The complete list of websites associated with the malware includes:
Search.babylon.com, scour.com, blinkx.com, Worldslife.com, Blendersearch.com, Bodisparking.com, coolsearchserver.com, webplains.net, find-fast-answers.com, search-netsite.com, toseeka.com, AboutBlank, La.vuwl.com, 10-directory.com, 63.209.69.107, 67.29.139.153, 7search.com, adorika.com, adf.ly, admarketplace.com, alive-finder.com, alltheservices.com, articlemule.org, asklots.com, ave99.com, b00kmarks.com, background-sleuth.net, bargainmatch.com, beoo.com, bestdiscountinsurance.com, bestsearchpage.com, bestclicksnow.com, bestmarkstore.com, bestwebchoices.com, bestwebsearch.com, bidsystem.com, secure.bidvertiser.com, britewallet.com, budgetmatch.net, buzzclick.com, celebrity-gossip.net, cheapstuff.com, citysearch.com, clicksor.com (Clicksor), clkads.com, feed.clickbizz.com, comparedby.us, comparestores.net, couponmountain.com, digitaltrends.com, easilyfindlocal.com, everythinghere.com, evoplus.com, expandsearchanswers.com (expand search answers), fastfinder.com, feedsmixer.org (starFeedsMixer), find-quick-results.com, FilesCup.com (FilesCup), findexmark.com, find-answers-fast.com, Zinkwink.com, us-srch-system.com, finditreport.com, findology.com, finderquery.com, findstuff.com, flurrysearch.com, forless.com, gimmeanswers.org, glimpse.com, google-redirect.com, googlesearchserver.net, get-search-results.com, goingonearth.com, goodsearch.com, gomeo.co.uk, gossipcenter.com, gquestionnaire.com, greatsearchserver.com, greenluo.com, grooveswish.com, guide2faucets.com, happili.com, HelloLocal.com, hyperpromote.com, informationgetter.com, inruo.com, jerseyscatalog.com, juggle.com, k100searches.com, YouPorn, liutilities.com, livejasmin.com (creative.livejasmin.com popups), local-search-pages.com, localpages.com, localsearchbug.com, lowpriceshopper.com, manufacturersdirectory.com, multifind24.com, mybestclick.net, mycustomsearch.cn, mydealchoices.com, mydealmatch.com, mylocalhero.com, neatsales.com, neatsearchserver.com (neat search server ZeroAccess rootkit), netsearchfinder.com, netshoppers.com, nexplore.com, privacycheck.ru, Pulse360.com, qooqle.com, questyes.com, quick-search-results.com, quick-suggest.com, redirectsite.net, results5.google.com, safecompare.com, saveandcoupon.com, savecompare.com, savingwithads.com, scoursearch.net, search-redirector.com, searchforall.info, searching4all.com, search-results.com (int.search-results.com), searchbacon.com, searchdiscovered.com, searchqu.com, searchqualitysites.com, searchnext.com, searchspice.com, shopcompare.net, shopcompareus.com, shopfinded.com, shopica.com, shopica.com/search, shopzilla.com, socialsurvey2011.info, Social Search Redirect, Search-netsite.com, kitchenrenopages.com, kingtopsearch.net, kiseek.com, lawyerinsight.org, letsbuystuff.com, njksearc.net, qooqlle.com, Storeordersonline.com, somesearchsystem.com, startnow.com, startsearcher.com, supersearchserver.com, TabDiscover.com, tazinga.com (tazinga!), theifinder.com, Thewebtimes.com, Marveloussearchsystem.com, merchantsnearby.com, monstermarketplace.com, mooter.com, TheTop10.com, tubedownloader.com, theyellowpages.com, theyellowpagez.com, topdaodrugs.com, tubedownloader.com, Therelatedsearch.com, unblock-us.com, valueapproved.com, vshare.toolbarhome.com (vShare), vehiclefind24.com, whatcarefreefeelslike.com,weeklycontestwinner.org, weeklyusa-winner.com, webshoppinghelper.com, webresults6.org, yellowmoxie.com, search.yellowise.com, ylwbook.addresses.com, youfindmore.com and Zwankysearch.com.
Not all malware announces its presence, but unless you changed your own host file, you can be certain you have a browser hijacker or Google Redirect Virus when your search requests forcibly routes you to unwanted websites. Cybercriminals create malware to multi-task and achieve one or more payloads. The foreign websites may include links that yield cybercrooks unearned pay-per-click (PPC) residuals or might help promote a rogue security program.
Google Redirect Virus has rootkit characteristics meaning it may go undetected from many applications. Google Redirect Virus can be said to be very similar to the parasites and fake security applications known as Alureon, Windows Necessary Firewall and even Fast Windows Antivirus 2011.
The longer you tolerate the presence of a Google Redirect Virus on your computer, the higher the risk of severe damage to your data and system as these malicious programs use a lot of resources and could lead to a complete system crash. Therefore, you should not waste time, letting hackers steal your personal information and destroying your computer. Instead, purchase a reliable anti-malware program that is capable of digging into the root of your system to find and clear all traces of the Google Redirect Virus.
In the meantime, you are advised to disconnect your device from the Internet to prevent any new transmissions of data to a remote server. You should also use a malware-free PC to change your logins and security credentials for all your online accounts.
Malware exploits vulnerabilities found in software or hardware or takes advantage of human behavior and the ignorance of executing Internet security practices. So if you or someone using your PC indulged in one of the following, it could explain how your PC got infected with the Google Redirect Virus.
- You took your chances and decided against installing a reputable anti-malware tool.
- You installed an anti-malware tool but got comfortable and did not renew it.
- You were drawn into clicking on a dubious link of some online suicide or
celebrity hoax. - You were spammed because you didn't verify the source of that email attachment or link from
your family or friend, whose accounts was hijacked by a cybercriminal. - You love the word free and pirated music or movies.
- You love freeware and shareware and downloaded an infectious codec to view a movie or video.
- You love visiting porn sites, gaming sites or warez ones and got infected.
To combat malware short and long-term is to understand its structure and malicious intent. Below is a general outline of what is in store for PCs housing the Google Redirect Virus:
- Trojan gains deceptive entry by exploiting vulnerabilities in hardware, software or good ole human behavior and weak Internet security practices.
- Modifies system registry and makes an entry so that its random named executable (done to keep the Internet security community guessing) is run at every boot.
- Drops a .TMP file in your temporary folder and this file installs other malicious components.
- The .TMP file (randomly named) will register itself as a legitimate service (thus bypassing your firewall and eluding AVG efforts) by copying a legitimate .dll file and infusing it with its poisonous script to load its malicious .TMP file.
- It then exploits vulnerabilities in Microsoft Windows DLL listing by adding the 'modified' .dll file and having it loaded into memory along with the other 'legitimate' ones.
- Once loaded, the venomous .TMP file creates a randomly named file in your 'driver' folder (usually with the .sys extension). This random file is the component that hides all its malicious files and programs from prying eyes (yours and AVG radar).
- Once the random .sys file is deployed, it drops a .dll file in your 'system' folder and this file is then injected into the SVCHOST executable, which downloads more malicious components from the Internet. It is these configuration files that help a hacker do the following:
a. Perform HTTP transfers (i.e. to send or receive new transmissions)
b. Display or trigger pop-up adverts
c. Inhibit programs or applications from running, especially those threatening malicious attacks.
d. Set command delay
e. Order DNS attacks
f. Spoof email accounts and spam persons on contact list
g. Download other malicious programs such as:
i. Trojan keylogger = steal vital data out of cache or directly off-web based forms
ii. Trojan backdoor = exploit remote assistance tool to secretly make use of your PC
iii. Trojan hijacker = change your host files and redirect web searches to malicious or unwanted websites
iv. Trojan dropper = drop more malicious components or programs in your PC
In addition to the Google Redirect Virus hijacking your browser, your system may become impaired, and you might notice the following:
- Keyboard malfunctioning
- Windows will unexpectedly requests reactivation of drivers
- System runs slow or freezes up
- Applications do not run properly
- Homepage changed or browser redirects you to unwanted websites
- Icons added or missing and hardware or drivers inoperable
The longer you allow the Google Redirect Virus to fester, the bigger the risk or threat to your data and system, as these malicious programs use a lot of resource and could cause a system crash.
However, don't be surprised if you are assaulted by pop-ups adverts or scary alerts and fake warnings, or if a slick-looking interface appears out of nowhere and runs an unauthorized scan. This is the typical behavior of a rogue security program, a well-used scam used to scare PC users into blindly handing over their credit card and bank routing number to buy a useless piece of software. Never trust any program that self-loads, runs an unauthorized scan or hijacks your browser.
Don't waste time and don't let some hacker steal your personal information. Fight fire with fire by using a reliable anti-malware tool that is capable of digging into the root of your system and finding all traces of the Google Redirect Virus.
In the interim, disconnect your Internet to stop any new transmissions of data to some remote server. Get to a malware-free PC and change your logins and security credentials for your online accounts.

Aliases
15 security vendors flagged this file as malicious.
| Anti-Virus Software | Detection |
|---|---|
| Panda | Trj/Genetic.gen |
| AVG | Generic29.AKVZ |
| Fortinet | W32/Kryptik.KO!tr |
| Ikarus | Win32.Malware |
| AhnLab-V3 | Trojan/Win32.Milicenso |
| Microsoft | Trojan:Win32/Vundo |
| AntiVir | TR/Crypt.ZPACK.Gen2 |
| Comodo | UnclassifiedMalware |
| Kaspersky | HEUR:Trojan.Win32.Generic |
| ClamAV | WIN.Trojan.Agent-83670 |
| Symantec | WS.Reputation.1 |
| K7AntiVirus | Trojan |
| McAfee | Artemis!A99D0C59FDB7 |
| CAT-QuickHeal | Trojan.Vundo.Gen |
| Panda | Generic Malware |
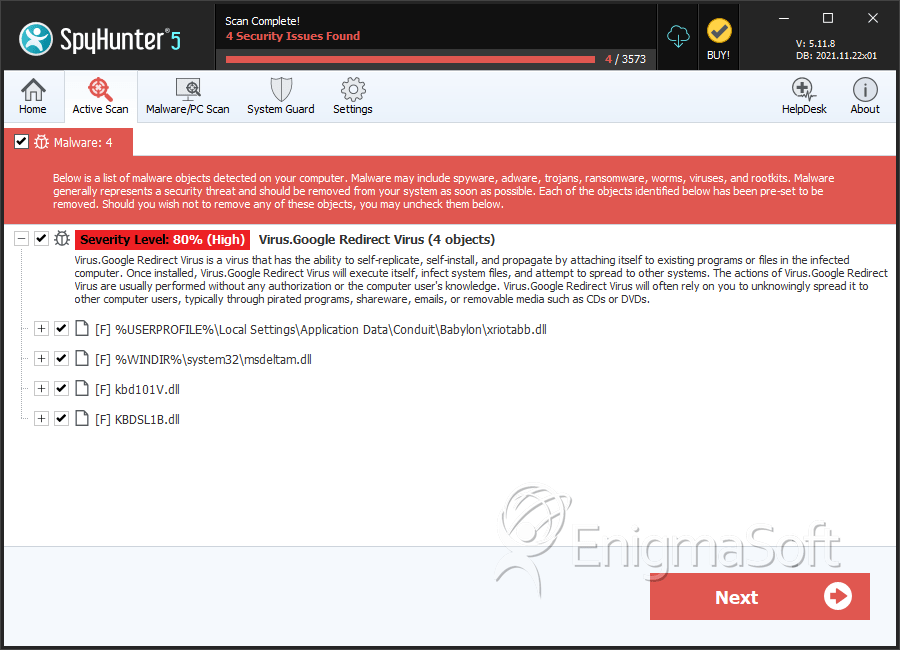
SpyHunter Detects & Remove Google Redirect Virus
File System Details
| # | File Name | MD5 |
Detections
Detections: The number of confirmed and suspected cases of a particular threat detected on
infected computers as reported by SpyHunter.
|
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | xriotabb.dll | 2a69d434d9d6d6d120fc39a190ca00d3 | 102 |
| 2. | msdeltam.dll | 0517f1b0c76bd2a32f0cb681617bee80 | 17 |
| 3. | TDSSserv.sys | ||
| 4. | C:\WINDOWS\system32\uacinit.dll | ||
| 5. | C:\WINDOWS\SYSTEM32\4DW4R3.dll | ||
| 6. | C:\WINDOWS\SYSTEM32\DRIVERS\4DW4R3.sys | ||
| 7. | C:\WINDOWS\Xzagua.exe | ||
| 8. | Xwo.exe | ||
| 9. | C:\Windows\System32\wdmaud.sys | ||
| 10. | C:\WINDOWS\system32\UAC.dll | ||
| 11. | C:\WINDOWS\SYSTEM32\4DW4R3c.dll | ||
| 12. | C:\WINDOWS\system32\drivers\UAC.sys | ||
| 13. |
C:\Documents and Settings\ |
||
| 14. | Xwk.exe | ||
| 15. | dmgsh.exe | ||
| 16. | C:\WINDOWS\_VOID\_VOIDd.sys | ||
| 17. | C:\WINDOWS\system32\_VOID.dll | ||
| 18. | C:\WINDOWS\system32\drivers\_VOID.sys | ||
| 19. | Xzagua.exe | ||
| 20. | C:\WINDOWS\system32\UAC.dat | ||
| 21. | C:\WINDOWS\SYSTEM32\4DW4R3sv.dat | ||
| 22. | %Temp%\UAC.tmp | ||
| 23. | C:\WINDOWS\system32\UAC.db | ||
| 24. | C:\WINDOWS\system32\_VOID.dat | ||
| 25. | C:\WINDOWS\Temp\UAC.tmp | ||
| 26. | C:\WINDOWS\_VOID\ | ||
| 27. | C:\WINDOWS\system32\uactmp.db | ||
| 28. | C:\WINDOWS\Temp\_VOIDtmp | ||
| 29. | %Temp%\_VOID.tmp | ||
| 30. | kbd101V.dll | a99d0c59fdb79c60d748b35f3ec3e448 | 0 |
| 31. | KBDSL1B.dll | 6f1ad64ccb0b277c0668318e20ef27fc | 0 |

