Cronus Ransomware
In the digital age, the threat of malware, particularly ransomware, is a significant concern for individuals and organizations alike. Ransomware, a threatening software designed to block access to a computer or data until a ransom is paid, can cause substantial harm. Understanding and protecting against such threats is crucial to safeguard personal and professional data.
Table of Contents
Understanding the Cronus Ransomware
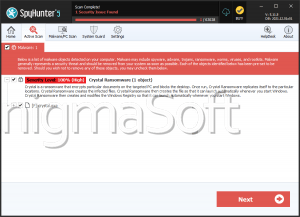
The Cronus Ransomware is a notable example of a modern ransomware threat. Upon infection, Cronus encrypts files on the victim's machine and changes their extensions to five random characters, making the files inaccessible. For instance, '1.doc' might be renamed to '1.doc.dO6qm,' and '2.pdf' to '2.png.6mPyE.' This renaming process obfuscates the file types and contributes to the overall disruption caused by the malware.
The Ransom Note and Threats
After encryption, the Cronus Ransomware changes the desktop wallpaper and leaves a ransom note named 'cronus.txt.' This note claims that the encrypted files have been secured using AES-256-CBC/RSA-2048 encryption algorithms and asserts that personal data, including passwords and emails, has been collected. The note threatens violence against the victim and their loved ones, urging immediate compliance with the ransom demands.
The attackers demand a payment of $500 in Bitcoin, instructing victims to send the transaction ID to the email address redroomowner@dnmx.org. They promise to provide a decryption tool upon payment, although there is no guarantee that paying the ransom will result in file recovery.
Impact and Recovery Challenges
Recovering files encrypted by Cronus without paying the ransom is often challenging. While data backups or third-party decryption tools may occasionally offer a solution, they are not always available or effective. Cybercriminals typically possess the only tools capable of decryption, placing victims in a difficult position. However, paying the ransom is strongly discouraged as it does not guarantee file recovery and may encourage further criminal activity.
How Cronus Spreads?
The Cronus Ransomware, like many others, can spread through various methods:
- Exploiting Vulnerabilities: Attackers often exploit weaknesses in outdated software or operating systems.
- Phishing Emails: Fraudulent emails containing malicious attachments or links are a common vector for ransomware distribution.
- Technical Support Frauds and Fraudulent Advertisements: Tactics and advertisements that mislead users into downloading malware are frequently employed.
- Pirated Software: Downloading pirated software, including cracking tools and key generators, can lead to ransomware infections.
- P2P Networks and Compromised Websites: Ransomware may also spread through peer-to-peer networks and deceptive or compromised websites.
- Infected USB Drives: Physical media, such as USB drives, can be used to transfer ransomware to a target computer.
Security Measures to Protect against Ransomware
To safeguard against ransomware like Cronus, users should implement comprehensive security measures:
- Regular Backups: Keep regular backups of necessary data on an outside server or unplugged storage device. This ensures data can be restored without paying a ransom.
- Update Software: Preserve your operating systems, software and applications updated to protect against known vulnerabilities.
- Email Caution: Be wary of unsolicited emails, especially those containing attachments or links. Verify the sender's identity before opening any such email.
- Security Software: Use reputable anti-malware software to detect and prevent ransomware infections.
- Network Security: Implement network security measures, including firewalls and intrusion detection tools, to monitor and protect against malicious activity.
- Educate and Train: Educate employees and family members about the numerous risks of ransomware and the safe online practices they should implement.
The Cronus Ransomware exemplifies the destructive potential of ransomware attacks, emphasizing the importance of robust security practices. By understanding the methods used by threat actors and implementing preventative measures, users can lessen the risk of ransomware infections and protect their valuable data from cybercriminals.
The ransom note left to the victims of the Cronus Ransomware reads:
'Warning, your files are encrypted by Cronus.
This is not a threat, this is a fact:
Your files have been encrypted with AES CBC 256 / RSA 2048 algorithm.
We have obtained extensive data, including passwords, e-mails and more.
We will shoot you and your extended family, pets and friends to death.
However, calm down, because you have a month to act on our desires.
How do I get spared:
Collect $500 in Bitcoin, an untraced anonymous cryptocurrency.
Send the specified amount to: 16JpyqQJ6z1GbxJNztjUnepXsqee3SBz75
Send the transaction ID to our e-mail: redroomowner@dnmx.org
You will later be mailed your decryption tool along with a safety certificate.
WARNING:
If you do not pay, you will be put into a darkweb livestream with spectators.
Users can pay to torture you in any way, provided that they pay enough.
Our users CAN and WILL cut your fingers off and kill your pets in front of you!'