Trojan.Zbot
Threat Scorecard
EnigmaSoft Threat Scorecard
EnigmaSoft Threat Scorecards are assessment reports for different malware threats which have been collected and analyzed by our research team. EnigmaSoft Threat Scorecards evaluate and rank threats using several metrics including real-world and potential risk factors, trends, frequency, prevalence, and persistence. EnigmaSoft Threat Scorecards are updated regularly based on our research data and metrics and are useful for a wide range of computer users, from end users seeking solutions to remove malware from their systems to security experts analyzing threats.
EnigmaSoft Threat Scorecards display a variety of useful information, including:
Popularity Rank: The ranking of a particular threat in EnigmaSoft’s Threat Database.
Severity Level: The determined severity level of an object, represented numerically, based on our risk modeling process and research, as explained in our Threat Assessment Criteria.
Infected Computers: The number of confirmed and suspected cases of a particular threat detected on infected computers as reported by SpyHunter.
See also Threat Assessment Criteria.
| Popularity Rank: | 9,171 |
| Threat Level: | 80 % (High) |
| Infected Computers: | 2,282 |
| First Seen: | July 24, 2009 |
| Last Seen: | January 20, 2026 |
| OS(es) Affected: | Windows |
Trojan.Zbot is a fairly generic backdoor Trojan infection that is closely linked to Mal/VB-AER and the Zeus Trojan, one of the most infamous malware infections. Since 2007, Trojan.Zbot has made headlines when Trojan.Zbot was used to infiltrate and steal information from the Transportation Department of the United States. Since March of 2009, Trojan.Zbot and the Zeus Trojan became widespread, infecting millions of computer from all around the world. ESG security researchers detected thousands of FTP servers of some of the most popular websites that were infected with the Zeus Trojan and Trojan.Zbot. Malware analysts estimate that the botnets associated with Trojan.Zbot cost billions of dollars every year and that a large percentage of phishing messages on Facebook and in spam emails are sent in order to spread malware associated with Trojan.Zbot. In the fall of 2010, the FBI cracked down on the criminal network thought to be responsible for an attack using Trojan.Zbot and the Zeus Trojan that resulted in the theft of more than seventy million dollars from American banks. About ninety people were arrested in relation to these criminal acts in the United States, the Russian Federation, the United Kingdom and Ukraine. In 2011, PC security researchers are facing a serious challenge since the source code of Zeus Trojan and Trojan.Zbot were leaked to the public, enabling practically anyone to use Trojan.Zbot to perform their own attacks.
Table of Contents
Is Your Computer System in Danger from Trojan.Zbot?
While malware associated with Trojan.Zbot is not confined to a single area, the five countries with the highest incidence of infection are Mexico, Egypt, Saudi Arabia, the United States and Turkey. As of today, this malware infection is linked to the largest botnets known to PC security researchers. If your operating system is not Windows, then you are safe from Trojan.Zbot. This malware infection can only attack computer system with the Windows Operating system. Users of Windows Vista and Windows Vista SP1 operating systems are particularly vulnerable and form the majority of computer systems integrating this network of infected computers. Each criminal can fine tune their infection in order to steal different data, although Trojan.Zbot is mostly linked to credit card and online banking account information theft. However, these can also be used to steal login information for email or social media accounts.
Aliases
15 security vendors flagged this file as malicious.
| Antivirus Vendor | Detection |
|---|---|
| AVG | Generic7_c.BULS |
| Fortinet | W32/Bublik.AKIQ!tr |
| Ikarus | Backdoor.Win32.DarkKomet |
| AhnLab-V3 | Trojan/Win32.Jorik |
| McAfee-GW-Edition | Heuristic.BehavesLike.Win32.Suspicious-BAY.S |
| AntiVir | TR/Rogue.8877826.1 |
| Kaspersky | Trojan.Win32.Bublik.akiq |
| Avast | AutoIt:MalOb-J [Trj] |
| McAfee | Artemis!1C946EE5948C |
| AVG | Generic32.CDAA |
| Ikarus | Trojan.Win32.Spy2 |
| Kaspersky | Trojan-Dropper.Win32.Agent.hjwv |
| Fortinet | W32/Jorik_Zbot.PLC!tr |
| McAfee-GW-Edition | Heuristic.BehavesLike.Win32.ModifiedUPX.C |
| AntiVir | TR/Symmi.18703.2 |
SpyHunter Detects & Remove Trojan.Zbot
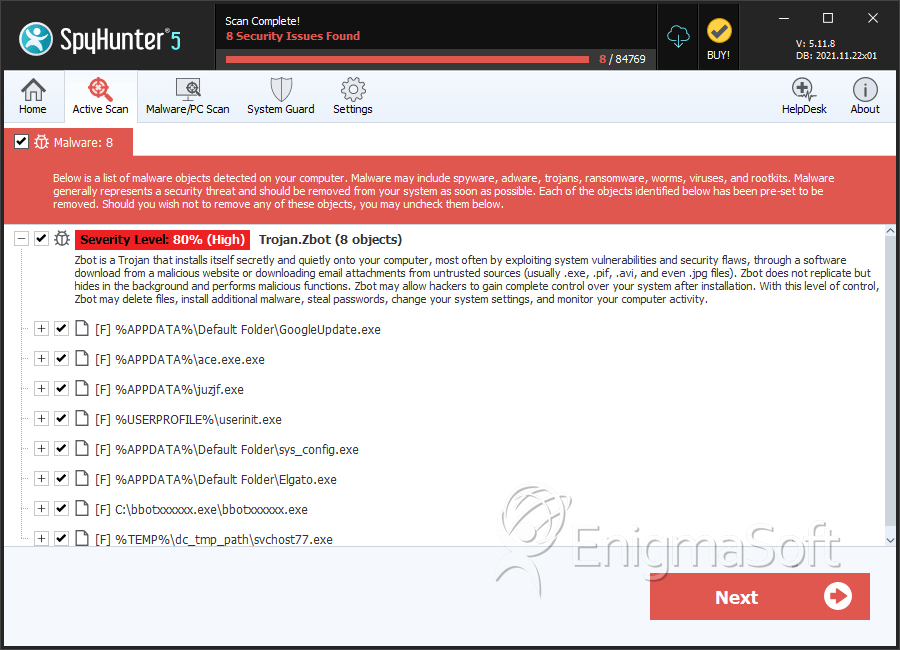
File System Details
| # | File Name | MD5 |
Detections
Detections: The number of confirmed and suspected cases of a particular threat detected on
infected computers as reported by SpyHunter.
|
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | GoogleUpdate.exe | de75d9858dd25f83ee666c4890367023 | 157 |
| 2. | ace.exe.exe | 2af6923df61c3800fb4957cd5163646d | 118 |
| 3. | sys_config.exe | 2c770a08cf50a31e138aa505c81a8cb4 | 40 |
| 4. | Elgato.exe | d9a57b7f55011099f22eac398f8683a3 | 20 |
| 5. | bbotxxxxxx.exe | 02d7b03f126ced200af04cafffbf4f66 | 18 |
| 6. | svchost77.exe | 4063dc3346591414467dea192e4de47d | 17 |
| 7. | server.exe | 1c946ee5948c6d23847688c7d5fb8ebd | 15 |
| 8. | Default File.exe | ce9a0cdd7f5f3a46c13e8001db1fc4b4 | 14 |
| 9. | Defcon.exe | 02dbd6164feb882e0c5fbd546ded3781 | 13 |
| 10. | wgsdgsdgdsgsd.exe | d4c60f32496ae92c5a53bda45d28937d | 9 |
| 11. | crss.exe | 733032ca6f13e38740fc4416eee0a0d4 | 9 |
| 12. | svchost.exe | 472732bcf7067db19136591db7694678 | 8 |
| 13. | _ex-08.exe | 4d9a644bb19c3d1fd158aed7830a457e | 7 |
| 14. | oshdo.dll | 267433320dc37f9369aef2aeaae68499 | 5 |
| 15. | 0.0863059484879578.exe | b3f35490864b39475bd5d8e9a12a0f08 | 3 |
| 16. | Recycle.Bin.exe | 5ed168874559f43720d9a79b20c89d9f | 3 |
| 17. | B6232F3A6E7.exe | 96cb97d9c4f61ab61cfad5a60606f242 | 3 |
| 18. | 0.2778958902928622.exe | f4f2bd07bfaf360b2ba596d134df76e3 | 2 |
| 19. | auaucdlve.exe | cab45be12136d15f2958b1ca575131b4 | 2 |
| 20. | ntos.exe | 9893493ec0578ac0194366a4e027e829 | 2 |
| 21. | MaelXpers.exe | a69349baf03c5a5f8dac25232ae55a8d | 2 |
| 22. | 9E787BEFEC0.exe | c0397b8114fb367b3ea3d1a9d5bde409 | 1 |
| 23. | dcratnewfud.exe | e7fad45a14545e19debf752ebb4c7510 | 1 |
| 24. | {14003D43-1705-1636-2800-333714001D1F}.exe | 604fdaa1fd4e335f26032fd416a5461b | 1 |
| 25. | apijcajxv.exe | 70383d5dd9b91c425b0107cf1e6c7b55 | 1 |
| 26. | dwtray.exe | aa872cb97a821e7736ba479558acfe78 | 1 |
| 27. | shortcuts.exe | 5cb5a2617939cc2428f4f24b9f56421f | 1 |
| 28. | file.exe | 0efa791652688dba9b98a058f34f3fc8 | 1 |
Registry Details
URLs
Trojan.Zbot may call the following URLs:
| 2sdfhs8d7fsh34d8f7s.org |
| 51qn.net |
| av4321.us |
| batmu.cn |
| clicksurfcash.net |
| crisis1s.com |
| fordearfriends.com |
| hotdomainworld.info |
| kakajz.cn |
| lilj.us |
| sfqjsf.cn |
| skp360.com |
Analysis Report
General information
| Family Name: | Trojan.Zbot |
|---|---|
| Signature status: | Self Signed |
Known Samples
Known Samples
This section lists other file samples believed to be associated with this family.|
MD5:
124371998fe68456f2512121f9cd8f6e
SHA1:
598d02f8fe185c0372190306f2f17d6fb478e38f
SHA256:
F6A9C65B034CDABB55EA3BF7AEBD116EA913FD56CB32BB4AA85C902578DFD1BA
File Size:
2.21 MB, 2207752 bytes
|
Windows Portable Executable Attributes
- File doesn't have "Rich" header
- File doesn't have exports table
- File has TLS information
- File is 32-bit executable
- File is either console or GUI application
- File is GUI application (IMAGE_SUBSYSTEM_WINDOWS_GUI)
- File is Native application (NOT .NET application)
- File is not packed
- IMAGE_FILE_DLL is not set inside PE header (Executable)
- IMAGE_FILE_EXECUTABLE_IMAGE is set inside PE header (Executable Image)
File Icons
File Icons
This section displays icon resources found within family samples. Malware often replicates icons commonly associated with legitimate software to mislead users into believing the malware is safe.Windows PE Version Information
Windows PE Version Information
This section displays values and attributes that have been set in the Windows file version information data structure for samples within this family. To mislead users, malware actors often add fake version information mimicking legitimate software.| Name | Value |
|---|---|
| File Description | Option MFC 응용 프로그램 |
| File Version | 1, 0, 0, 1 |
| Internal Name | Option |
| Legal Copyright | Copyright (C) 2002 |
| Original Filename | Option.EXE |
| Product Name | Option 응용 프로그램 |
| Product Version | 1, 0, 0, 1 |
Digital Signatures
Digital Signatures
This section lists digital signatures that are attached to samples within this family. When analyzing and verifying digital signatures, it is important to confirm that the signature’s root authority is a well-known and trustworthy entity and that the status of the signature is good. Malware is often signed with non-trustworthy “Self Signed” digital signatures (which can be easily created by a malware author with no verification). Malware may also be signed by legitimate signatures that have an invalid status, and by signatures from questionable root authorities with fake or misleading “Signer” names.| Signer | Root | Status |
|---|---|---|
| Game Cafe Services Inc | SSL.com Code Signing Intermediate CA ECC R2 | Self Signed |
File Traits
- x86
Block Information
Block Information
During analysis, EnigmaSoft breaks file samples into logical blocks for classification and comparison with other samples. Blocks can be used to generate malware detection rules and to group file samples into families based on shared source code, functionality and other distinguishing attributes and characteristics. This section lists a summary of this block data, as well as its classification by EnigmaSoft. A visual representation of the block data is also displayed, where available.| Total Blocks: | 8,439 |
|---|---|
| Potentially Malicious Blocks: | 2 |
| Whitelisted Blocks: | 8,402 |
| Unknown Blocks: | 35 |
Visual Map
? - Unknown Block
x - Potentially Malicious Block
Similar Families
Similar Families
This section lists other families that share similarities with this family, based on EnigmaSoft’s analysis. Many malware families are created from the same malware toolkits and use the same packing and encryption techniques but uniquely extend functionality. Similar families may also share source code, attributes, icons, subcomponents, compromised and/or invalid digital signatures, and network characteristics. Researchers leverage these similarities to rapidly and effectively triage file samples and extend malware detection rules.- Agent.AIBB
- Farfli.ZA
- Marte.L
- Rugmi.GA
- Spy.Agent.XD
Show More
- YoutubeDownloaderGuru.B
Windows API Usage
Windows API Usage
This section lists Windows API calls that are used by the samples in this family. Windows API usage analysis is a valuable tool that can help identify malicious activity, such as keylogging, security privilege escalation, data encryption, data exfiltration, interference with antivirus software, and network request manipulation.| Category | API |
|---|---|
| Anti Debug |
|
| User Data Access |
|
| Other Suspicious |
|
