Petya 2017 Ransomware
Threat Scorecard
EnigmaSoft Threat Scorecard
EnigmaSoft Threat Scorecards are assessment reports for different malware threats which have been collected and analyzed by our research team. EnigmaSoft Threat Scorecards evaluate and rank threats using several metrics including real-world and potential risk factors, trends, frequency, prevalence, and persistence. EnigmaSoft Threat Scorecards are updated regularly based on our research data and metrics and are useful for a wide range of computer users, from end users seeking solutions to remove malware from their systems to security experts analyzing threats.
EnigmaSoft Threat Scorecards display a variety of useful information, including:
Ranking: The ranking of a particular threat in EnigmaSoft’s Threat Database.
Severity Level: The determined severity level of an object, represented numerically, based on our risk modeling process and research, as explained in our Threat Assessment Criteria.
Infected Computers: The number of confirmed and suspected cases of a particular threat detected on infected computers as reported by SpyHunter.
See also Threat Assessment Criteria.
| Threat Level: | 100 % (High) |
| Infected Computers: | 173 |
| First Seen: | March 25, 2016 |
| Last Seen: | August 17, 2022 |
| OS(es) Affected: | Windows |
The Petya 2017 Ransomware is a threat infection that has been targeting computers in Europe. The Petya 2017 Ransomware attacks have been taking place since the end of June 2017. The Petya 2017 Ransomware seems to be a sophisticated ransomware Trojan that is designed to infect computers belonging to businesses, organizations and Web servers. There are various parallels between the Petya 2017 Ransomware campaign and the WannaCry threat campaign, which claimed several high-profile victims earlier in 2017. Among the victims of the Petya 2017 Ransomware infection are the computers of the Chernobyl nuclear plant, according to reports received by malware analysts.
Table of Contents
Is the Petya 2017 Ransomware Related to the WannaCry Attack?
At this point, malware analysts suspect that there may be some connection with the WannaCry threat campaign. However, it is clear that the Petya 2017 Ransomware is a variant of the Petya ransomware family, a well-known ransomware Trojan that has been active for a while. The Petya 2017 Ransomware is a new variant that may have some connection to previous campaigns. It has been capable of infecting more than 2000 computers in a single day, making the Petya 2017 Ransomware a significant risk to computer users and their data. Currently, the Petya 2017 Ransomware attacks are concentrated in Europe, particularly targeting Ukraine, which makes it seem that the Petya 2017 Ransomware may be connected to a state-sponsored attack from Russia. One reason to believe this is that the Ukrainian power grid and utility companies have been targeted in this attack, and also have been targeted by other attacks from Russia. The sophistication of the Petya 2017 Ransomware also points to the fact that its creators may have significant resources, allowing them to carry out an attack of this magnitude.
The Consequences of a Petya 2017 Ransomware Attack
The Petya 2017 Ransomware has attacked several high-profile Ukrainian targets. Among these are the state telecommunications company, the electricity supplier, the municipal metro, the Ukrainian central bank, and the Kiev airport. The Petya 2017 Ransomware attack also has attacked the computers at the Chernobyl nuclear plant. All of the computers using the Windows operating system have shut down, and manual systems are being used to make sure the power plant continues to operate safely. However, not only Ukraine has been under attack. Other infections have shown up in the United States and in other countries, although these are isolated attacks and do not seem to have the sophistication or the targeted nature that the ones in Ukraine present. As of writing, a hospital in the United States was compromised in the Petya 2017 Ransomware attack. Some Russian companies also have fallen to the Petya 2017 Ransomware, including the Russian oil company Rosneft (which may put into question the idea that the Petya 2017 Ransomware is part of a state-sponsored attack). Important companies in Spain and the United Kingdom also have reported problems related to the Petya 2017 Ransomware infection.
The Petya 2017 Ransomware Ransom Payments and Reports
In the short time between when the Petya 2017 Ransomware attacks were first observed and the writing of this report, at least 20 payment transactions had been made related to the Petya 2017 Ransomware. The Petya 2017 Ransomware demands payments of $300 USD in BitCoins, and nearly $5000 USD had been posted to the BitCoin wallet associated with the Petya 2017 Ransomware in only a short time. At this time it is unclear exactly how the Petya 2017 Ransomware is being distributed. It is possible that the Petya 2017 Ransomware is exploiting a vulnerability in Windows that has not been patched yet. These attacks may, in some way, be related to the software vulnerabilities misappropriated from the NSA earlier in 2017, which also were responsible for the extent of WannaCry attacks.
SpyHunter Detects & Remove Petya 2017 Ransomware
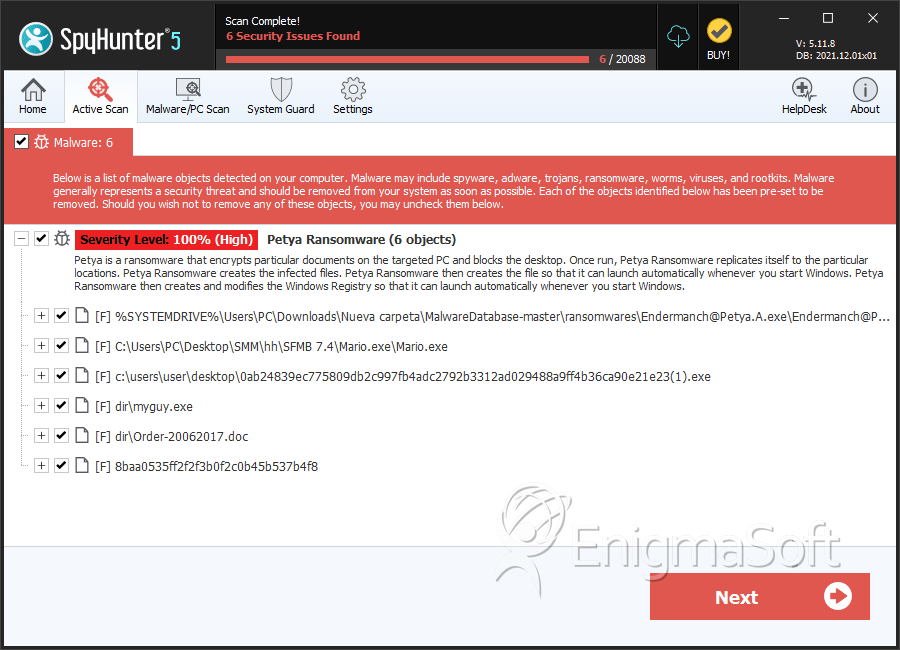
File System Details
| # | File Name | MD5 |
Detections
Detections: The number of confirmed and suspected cases of a particular threat detected on
infected computers as reported by SpyHunter.
|
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Endermanch@Petya.A.exe | af2379cc4d607a45ac44d62135fb7015 | 76 |
| 2. | Mario.exe | 71b6a493388e7d0b40c83ce903bc6b04 | 35 |
| 3. | myguy.exe | a1d5895f85751dfe67d19cccb51b051a | 1 |
| 4. | 0ab24839ec775809db2c997fb4adc2792b3312ad029488a9ff4b36ca90e21e23(1).exe | 16a2fd266cbf9d88fb359c82e9ff5bb3 | 1 |
| 5. | Order-20062017.doc | 415fe69bf32634ca98fa07633f4118e1 | 0 |
| 6. | 8baa0535ff2f2f3b0f2c0b45b537b4f8 | 8baa0535ff2f2f3b0f2c0b45b537b4f8 | 0 |


Submit Comment
Please DO NOT use this comment system for support or billing questions. For SpyHunter technical support requests, please contact our technical support team directly by opening a customer support ticket via your SpyHunter. For billing issues, please refer to our "Billing Questions or Problems?" page. For general inquiries (complaints, legal, press, marketing, copyright), visit our "Inquiries and Feedback" page.