Winsecure Ransomware
Threat Scorecard
EnigmaSoft Threat Scorecard
EnigmaSoft Threat Scorecards are assessment reports for different malware threats which have been collected and analyzed by our research team. EnigmaSoft Threat Scorecards evaluate and rank threats using several metrics including real-world and potential risk factors, trends, frequency, prevalence, and persistence. EnigmaSoft Threat Scorecards are updated regularly based on our research data and metrics and are useful for a wide range of computer users, from end users seeking solutions to remove malware from their systems to security experts analyzing threats.
EnigmaSoft Threat Scorecards display a variety of useful information, including:
Ranking: The ranking of a particular threat in EnigmaSoft’s Threat Database.
Severity Level: The determined severity level of an object, represented numerically, based on our risk modeling process and research, as explained in our Threat Assessment Criteria.
Infected Computers: The number of confirmed and suspected cases of a particular threat detected on infected computers as reported by SpyHunter.
See also Threat Assessment Criteria.
| Threat Level: | 100 % (High) |
| Infected Computers: | 7 |
| First Seen: | July 17, 2018 |
| Last Seen: | July 23, 2019 |
| OS(es) Affected: | Windows |
Winsecure Ransomware is a name that computer security experts use in reference to a file encoder Trojan that was identified on July 2nd, 2018. The Winsecure Ransomware Trojan was found on computers where the user loaded a fake Adobe Flash installer, which installed the threat to the Temp folder. The Winsecure Ransomware Trojan proved to be a customized version of the Bitshifter Ransomware that was added to security databases in July 2017. It appears that the creators of Bitshifter have been busy testing a new release of their product and they continue to use compromised legitimate servers to host their 'Command and Control' infrastructure.
The Winsecure Ransomware behaves like a generic crypto- threat and encodes data on the local disks. The Winsecure Ransomware includes routines for preventing PC users from restoring their data — the Shadow Volume snapshots and system restore points are deleted before the encryption process is initiated. Almost all ransomware samples feature instructions to delete the backups made by Windows. The Winsecure Ransomware is not very different from the NMCRYPT Ransomware and the AES-Matrix Ransomware. PC users may expect to find the '.encrypted' extension on files that have been encrypted by the threat. We have seen the Trojan to encode images, presentations, PDFs, databases, spreadsheets, MP3s and video using the AES cipher. Unfortunately, the decryption key is uploaded to remote servers and recovery of the data is impossible. For example, 'Cohenite Mineral.docx' is renamed to 'Cohenite Mineral.docx,' and you can find two foreign objects on your desktop named 'ransom_pay.html' and 'ransom_note.txt.' The files on your desktop are ransom notifications from the Winsecure team and offer the following:
'MOST OF YOUR IMPORTANT FILES HAVE BEEN
ENCRYPTED BY AES 256-CBC AND RSA 2048!
well, if you want to restore all your files you should send
!--PRICE-->0.05000000 BTC to the next address as you see below
!--BTC-->[1352RtNRpYRdKLWUUDkLBUKP7p4SqMAiTF]
!--TIME-->[a string with a set date and hour] (UTC)
if you do not have these hundreds of oil - you can say goodbye permanently to your files.
after payment files will be decrypted by himself. otherwise the key will be deleted.
you can decrypt for test any 3 files not more than 2 mb for each - just drop them to
'decrypt_folder' on your desktop. how to:
* turn off any AV
* payment
* keep your PC turned on
* wait for decryption
* get your files back
you'd could use any comfortable methods to make payment.
if cryptor was deleted, find 'c3cpxEASjsBJw2p8r9aynknfLspM7nFb.GolIum'
file on your desktop. change 'GolIum' to 'exe' and run that again.
don't make any changes for files.
good luck and have a nice day.
in code we trust'
Computer security researchers have seen the Winsecure Ransomware run as 'launcher.exe' on infected machines and demand 0.05 Bitcoin (326 USD/278 EUR) from users to decode their data. The threat operators may increase the ransom amount if they find out that their Trojan has compromised office computers. Compromised users might want to remove the Winsecure Ransomware with the help of a trusted cybersecurity instrument. AV engines support detection rules for Winsecure Ransomware and might mark related files with the following names:
Dropper.Agent.Win32.273122
Ransom_BITSHIFT.A
TR/FileCoder.suebo
Trojan-Ransom.Win32.Agent.izh
Trojan.Agent.ayah
Trojan.Generic.D56709E
Trojan.GenericKD.5664926
Trojan.Siggen7.25795
W32/Trojan.KQYJ-5474
Win32.Trojan.Dropper.Jmds
a variant of Win32/Filecoder.NMU
malware (ai score=100)
SpyHunter Detects & Remove Winsecure Ransomware
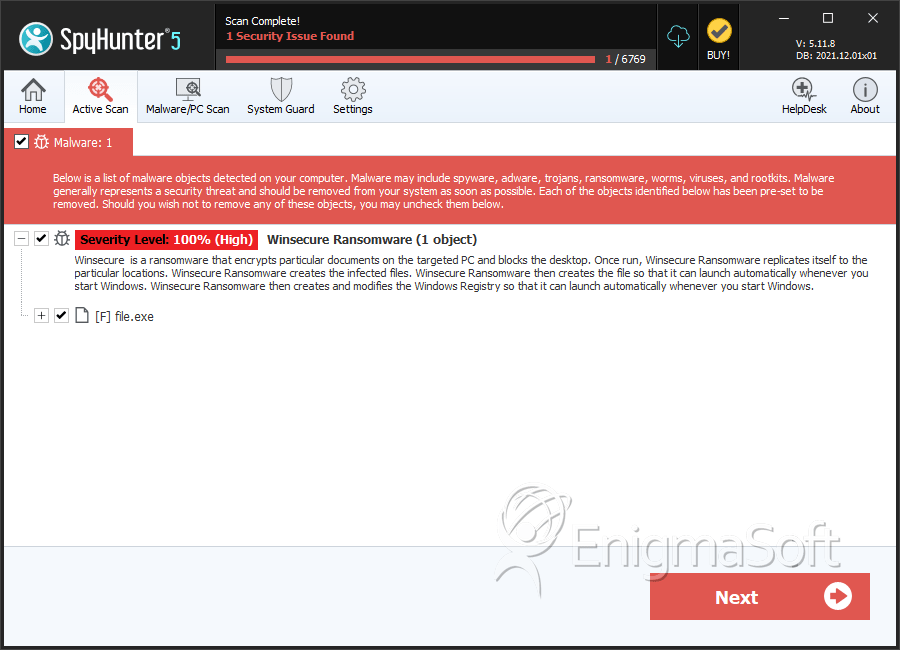
File System Details
| # | File Name | MD5 |
Detections
Detections: The number of confirmed and suspected cases of a particular threat detected on
infected computers as reported by SpyHunter.
|
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | file.exe | eca796d29e3acb940b3481f76100276e | 6 |


Submit Comment
Please DO NOT use this comment system for support or billing questions. For SpyHunter technical support requests, please contact our technical support team directly by opening a customer support ticket via your SpyHunter. For billing issues, please refer to our "Billing Questions or Problems?" page. For general inquiries (complaints, legal, press, marketing, copyright), visit our "Inquiries and Feedback" page.