SearchPageInstaller
The SearchPageInstaller software is a dubious application that is designed to target Mac systems. This utility's purpose is to plant advertisements on the websites that the user visits. It is rather fortunate that the SearchPageInstaller tool is only being used to inject advertisements in the sessions of the user because this utility can be utilized for the propagation of unsafe online tactics and phishing pages easily.
To plant advertisements in the sites visited by the victim, the SearchPageInstaller threat would install a third-party proxy service, which is then used to execute a so-called 'Man-in-The-Middle' attack. This approach allows the SearchPageInstaller threat to modify the contents of the websites that the user launches. The SearchPageInstaller malware utilizes a component called 'mitmproxy.' This component allows the SearchPageInstaller threat to meddle with both HHTP traffic and HTTPS traffic. To achieve the latter, the SearchPageInstaller threat impersonates certain certificates. However, the SearchPageInstaller threat may need the permission of its victims to gain access to their system. The users may be urged to enter their login credentials in a prompt that would authorize the changes in network settings initiated by the SearchPageInstaller threat. If you provide the SearchPageInstaller malware with the authorization it demands, you will allow it to have control over your network traffic.
Table of Contents
A New Generation of Adware
SearchPageInstaller also called SPI for short, is adware first spotted in the wild in 2017 at the earliest. The adware came back into the public eye recently when it was bundled together with mitmproxy as part of a new wave of attacks.
SPI takes a different approach than standard adware. Rather than sending users to an unwanted page, SPI adds advertisements to the top of HTML documents after users conduct an online search. The adware uses both HTTP and HTTPS proxies to do this. The evidence for this can be found in the System Preferences of an infected computer, as shown below:
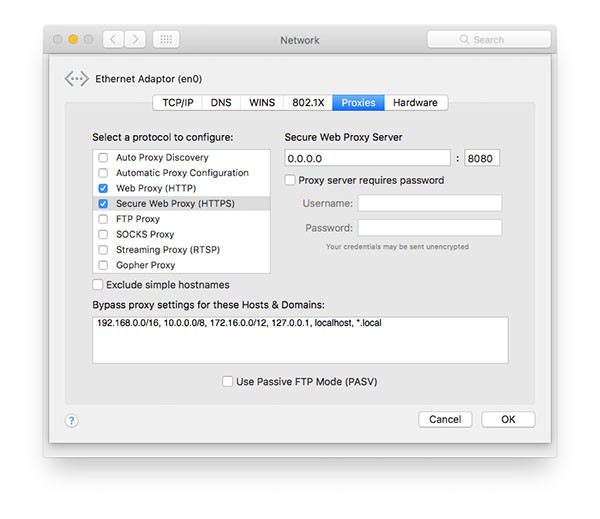
Inspecting a webpage affected by the virus shows that the script is edited to display advertisements from SPI instead of the adverts that would usually be shown:
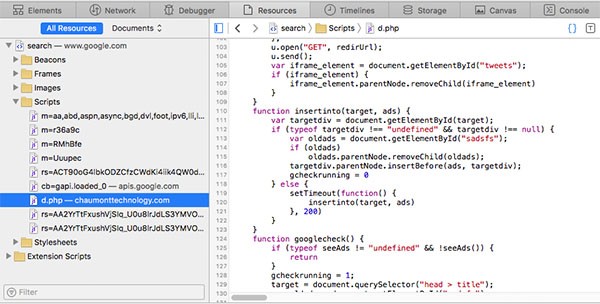
The Man in the Middle
SearchPageInstaller uses an open-source HTTPS proxy called mitmproxy to use an inject.py script to inject the script into the webpage.
The mitmproxy acts as a kind of main the middle between the client and server to create dummy certificates. These certificates convince the client that it is the server and the server that it is the client.
This change is made possible through the SearchPageInstaller binary, which manually installs the mitmproxy CA certificate after the user enters their password. Once authorized, the credentials necessary for the ‘man in the middle’ attack are created in the invisible mitmproxy folder.
What Does SearchPageInstaller Do?
The first thing SearchPageInstaller will attempt to do is get permission to install new certificates. From there, it changes the network proxy settings. This change requires admin approval, so it presents another authentication request.
If the adware is allowed to do as it pleases, it uses a mitmdump tool to view, record, and change HTTP traffic. The inject.py script is run with arguments that tell the proxy to ignore domains that fall within a specific regex pattern. This is likely to avoid problems with traffic protected by certificate pinning.
The primary purpose of SearchPageInstaller is to show users advertisements. Users click on the ads and generate money for the operator. There’s a high risk that some of these ads will be malicious and likely to install other viruses on a computer. Adware is one of the less dangerous forms of malware but, make no doubt about it; it’s still dangerous. That SPI can manipulate standard HTTP and encrypted HTTPS traffic is concerning, to say the least.

