Trojan.Tinba
Threat Scorecard
EnigmaSoft Threat Scorecard
EnigmaSoft Threat Scorecards are assessment reports for different malware threats which have been collected and analyzed by our research team. EnigmaSoft Threat Scorecards evaluate and rank threats using several metrics including real-world and potential risk factors, trends, frequency, prevalence, and persistence. EnigmaSoft Threat Scorecards are updated regularly based on our research data and metrics and are useful for a wide range of computer users, from end users seeking solutions to remove malware from their systems to security experts analyzing threats.
EnigmaSoft Threat Scorecards display a variety of useful information, including:
Ranking: The ranking of a particular threat in EnigmaSoft’s Threat Database.
Severity Level: The determined severity level of an object, represented numerically, based on our risk modeling process and research, as explained in our Threat Assessment Criteria.
Infected Computers: The number of confirmed and suspected cases of a particular threat detected on infected computers as reported by SpyHunter.
See also Threat Assessment Criteria.
| Threat Level: | 90 % (High) |
| Infected Computers: | 1,539 |
| First Seen: | June 4, 2012 |
| Last Seen: | February 16, 2023 |
| OS(es) Affected: | Windows |
Tinba is a banking Trojan whose purpose is to steal online banking credentials that victims enter in their browser. Tinba is primarily spread through malvertising campaigns, exploit kits and the ever-topical spam email campaigns. The main targets of the Trojan are bank customers residing in the United States and Europe.
The way Trojan.Tinba steals its victims online banking information is by using code injections that modify the portal pages of legitimate banking websites. The victim is presented with a very legitimate-looking, yet completely fake and malicious login interface for their respective bank. Using this login interface to enter sensitive data results in the login credentials being syphoned to the bad actors behind the Trojan.
Once the victim hits specific banking portals that are hard-coded in the malware, the original login interface is swapped with the malicious one through web injection. The web code injections are kept on the victim's hard drive and are encrypted using a key. The key itself is the name of the directory where the injection files are kept. Once it needs to inject the malicious code, Tinba decrypts it entirely and injects it in the browser's memory footprint with no other safety measures, which makes spotting the issue relatively easy for security researchers. The code injection itself and the fake info-stealing login interface use code that is very similar to that used by the Zeus banking Trojan.
Tinba is also known for resorting to social engineering tactics to urge its victims to enter their credentials in the fake login forms, even if the user did not originally intend to do any online banking. Such tactics include fake messages that the victim received an erroneous bank transfer and needs to refund the sum immediately, to avoid further trouble. Similar scare tactics are used by a lot of other types of malware, including rogue antivirus software and some niche cases of ransomware that attempt to scare the user into submission.
Table of Contents
SpyHunter Detects & Remove Trojan.Tinba
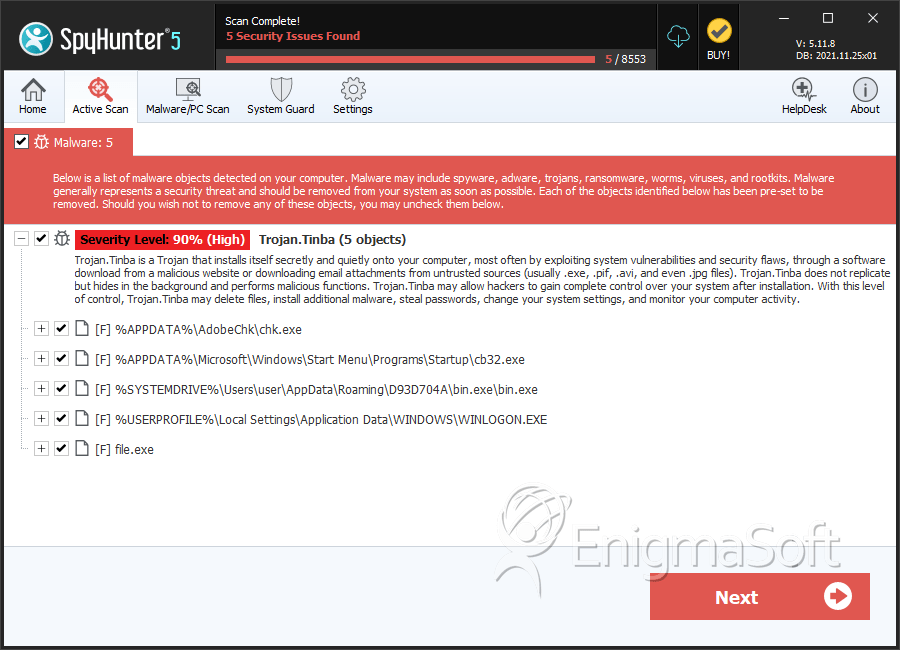
File System Details
| # | File Name | MD5 |
Detections
Detections: The number of confirmed and suspected cases of a particular threat detected on
infected computers as reported by SpyHunter.
|
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | chk.exe | 34c809f63528376356a5d85795f5ae22 | 224 |
| 2. | chk.exe | 42e844df5f940c6e1975ff7ebf4ba26a | 171 |
| 3. | chk.exe | 15159e7dce479b2d5e378f16af68af2e | 132 |
| 4. | chk.exe | 4a98ff2dc2428e00cc9d62d174d449b6 | 132 |
| 5. | chk.exe | da6115918cdcf1bf94701330655f059a | 123 |
| 6. | chk.exe | 043eeec8f688100ac142f6b344c19ef8 | 96 |
| 7. | chk.exe | e16f974e3def7d9c16aa61f60a26abd7 | 74 |
| 8. | chk.exe | a18096552f1f7faedde02d4236c7a095 | 71 |
| 9. | chk.exe | 5e00fd790838796332d2c754ef7b8dd0 | 59 |
| 10. | chk.exe | 3ab9d894bfb21c2143c6b4b29e7a435c | 50 |
| 11. | chk.exe | 70e91a8ef84783adc3c550bf3d5969f3 | 47 |
| 12. | chk.exe | d9f235cdf96453e74d184b7f5d1048a6 | 41 |
| 13. | chk.exe | 08ab359905a8316f9d86f0fd67b732a1 | 35 |
| 14. | chk.exe | b03787ba7021fb1394f6579a8f511ab3 | 32 |
| 15. | bin.exe | f6c5c74dd6805accbf57529b5214b3e0 | 4 |
| 16. | WINLOGON.EXE | 1e100c5435a8025e5bf471b09ec1a151 | 3 |
| 17. | file.exe | 08ab7f68c6b3a4a2a745cc244d41d213 | 1 |
| 18. | %SystemDrive%\Documents and Settings\All Users\Application Data\default\bin.exe | ||
| 19. | %SystemDrive%\Documents and Settings\All Users\Application Data\default\web.dat |


Submit Comment
Please DO NOT use this comment system for support or billing questions. For SpyHunter technical support requests, please contact our technical support team directly by opening a customer support ticket via your SpyHunter. For billing issues, please refer to our "Billing Questions or Problems?" page. For general inquiries (complaints, legal, press, marketing, copyright), visit our "Inquiries and Feedback" page.