Trojan.Genome
Threat Scorecard
EnigmaSoft Threat Scorecard
EnigmaSoft Threat Scorecards are assessment reports for different malware threats which have been collected and analyzed by our research team. EnigmaSoft Threat Scorecards evaluate and rank threats using several metrics including real-world and potential risk factors, trends, frequency, prevalence, and persistence. EnigmaSoft Threat Scorecards are updated regularly based on our research data and metrics and are useful for a wide range of computer users, from end users seeking solutions to remove malware from their systems to security experts analyzing threats.
EnigmaSoft Threat Scorecards display a variety of useful information, including:
Ranking: The ranking of a particular threat in EnigmaSoft’s Threat Database.
Severity Level: The determined severity level of an object, represented numerically, based on our risk modeling process and research, as explained in our Threat Assessment Criteria.
Infected Computers: The number of confirmed and suspected cases of a particular threat detected on infected computers as reported by SpyHunter.
See also Threat Assessment Criteria.
| Ranking: | 12,045 |
| Threat Level: | 80 % (High) |
| Infected Computers: | 687 |
| First Seen: | January 19, 2011 |
| Last Seen: | August 29, 2023 |
| OS(es) Affected: | Windows |
Even if you are careful and have anti-malware protection installed on your computer, you can still sometimes get infected with harmful malware. Several anti-malware researchers have identified Trojan.Genome as part of the Trojan family of malware and, if you are unfortunate enough to have Trojan.Genome slink into your system, Trojan.Genome will try to download surreptitiously and install other programs automatically. Trojans, in general, try to lead you up to clicking on harmful links or download infected programs. In most cases, Trojan.Genome may lead up to with contaminating your machine with more infections, so it is advisable you take measures of removing the said Trojan – the longer Trojan.Genome persists on your system, the more opportunities Trojan.Genome has to accomplish its payload.
Table of Contents
Getting Acquainted with Trojan.Genome
It is very often the case of malignant threats on the Internet being recognized under different aliases. Regarding Trojan.Genome, you should be aware that you may also come across Trojan.Genome under the guise of other names, such as Trojan.Win32.Genome.pruk, TrojanDownloader:Win32/Genome.AS, Win32.Genome and Trojan.Win32.Genome.afoso. The affected systems are ones that run on the Windows OS, like Windows Vista, Windows 7 and Windows 8.
One of the problems that you can find yourself struggling with is that Trojan.Genome is by its nature very resistant to removal. If you do not remove it completely, Trojan.Genome will just restore itself to its original condition, upon system reboot. To further add to your headaches, Trojan.Genome will usually slip past the detection of your anti-malware software of choice with the help of a rootkit, as the job a rootkit is to hide stealthily the existence of certain processes or programs. The Trojan will also make use of its ability to write an entry in the Master Boot Record (MBR) of Windows so that Trojan.Genome can automatically run after you boot up or restart your PC.
If you need to of know if you are infected with Trojan.Genome is to look for a particular file on your hard disk drive. Just do a simple search and find ‘utdqhz5i9inix.exe’ and ‘zlsrbvjm.exe’ (please note that even if you do not find these files on your system you may still be infected, as the malware usually creates files with different and random names).
How to Prevent Infection with Trojan.Genome
To avoid all the difficulties that Trojan.Genome brings to your way you should never get infected with Trojan.Genome at all. To achieve it, you need to know the methods Trojan.Genome uses to infiltrate its intended target. Most often the Trojan permeates into a targeted computer's OS with the help of spam e-mails, which include attached .zip extension files or contain detrimental links. There is also the chance of exposure to Trojan.Genome through the means of another malware that has already penetrated your system. Although this applies to most of the malware on the Internet, Trojan.Genome can also be hidden away in other freeware or shareware products that you download.
Other measures that you can take to prevent infection are the typically recommended in these situations, such as having up-to-date anti-malware software, be well-informed about Trojan.Genome and how Trojan.Genome functions, and turning on your firewall, although the effect of each measure may vary. In particular, Trojan.Genome edits the approved programs in the firewall's list and adds its own .exe so that Trojan.Genome has free rein in your system.
The Adverse Effects of Trojan.Genome
Any personal experience with computer malware is almost always to be a negative one. Trojan.Genome is no exception to the rule, as Trojan.Genome affects your PC in a negative way. Having this particular malware roam free in your OS will lead to a slower computer performance, resulting from excessive use of hardware resources. In addition to that, users have reported receiving a BSOD (Blue Screen of Death) and frequent computer freezes. Some malware researchers have reported that Trojan.Genome may try to contact a third-party host, using port 80 – dc540.4shared.com, dc602.4shared.com, google.com.br, to name a few. The reasons for that are several and may vary:
- To check if you are connected to the Internet.
- To send information about new infections.
- To receive configuration or other data.
- To download updates or other malware.
- To receive particular instructions, or
- To send personal data from the infected computer.
Unlike other malware that is out there on the Internet, Trojan.Genome isn't as harmless as some adware, for example, and you should exercise caution if you have fallen victim to the Trojan and pursue means of its removal.
SpyHunter Detects & Remove Trojan.Genome
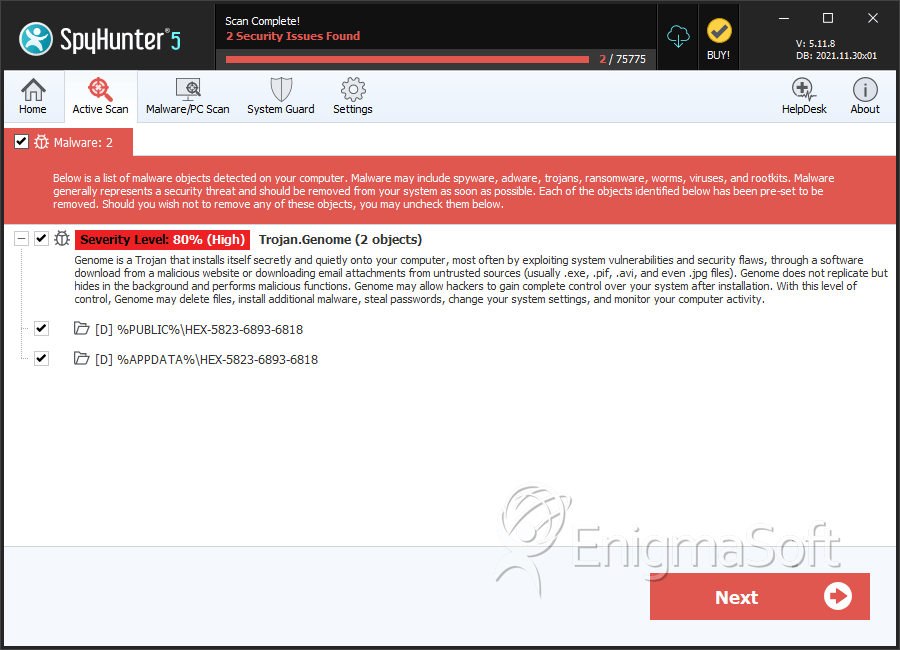
Directories
Trojan.Genome may create the following directory or directories:
| %APPDATA%\HEX-5823-6893-6818 |
| %PUBLIC%\HEX-5823-6893-6818 |


Submit Comment
Please DO NOT use this comment system for support or billing questions. For SpyHunter technical support requests, please contact our technical support team directly by opening a customer support ticket via your SpyHunter. For billing issues, please refer to our "Billing Questions or Problems?" page. For general inquiries (complaints, legal, press, marketing, copyright), visit our "Inquiries and Feedback" page.