Are You Sure You’re NOT Infected with Malware?
Don’t Fall Victim to Malware or Ransomware Attacks!
Detect and remove malware, viruses, ransomware & other threats for FREE! Get Protected with SpyHunter.
Download SpyHunter (FREE Trial!)*Mobile malware refers to types of security threats that affect mobile devices. It does not matter whether you have an Android or an Apple device; both can be susceptible to potential security risks. The rise of mobile malware is associated with the global growth of smartphone users. Mobile devices make it a lot easier to access corporate networks as opposed to landlines, and so, they become indispensable in everyone’s daily life. However, when something becomes so popular, it is inevitable that there will be parties trying to exploit it, too.
Mobile Device Vulnerabilities
Mobile malware cannot boast of the same numbers and the all-encompassing scope as computer malware, but it, more or less, follows the same patterns. First, it will try to exploit critical mobile software vulnerabilities, and a whopping 95% of Android devices could be hacked with a text message alone.
What’s more, although Apple devices are thought to be safer on average, they are not impervious to such attacks. Apple devices can get attacked by mobile malware through the official app store. Apple has vaunted protection, but malicious apps that target Apple devices are programmed in a way that they can be difficult to detect, and they might also come aboard piggybacking on legitimate apps. Thus, anyone should be aware that by owning a mobile device, they could always be exposed to a variety of security risks.
Mobile Malware Types
Just like we have a whole list of the most prominent types of PC malware, there are also groups of popular types of mobile malware. The most common ones are as follow:
Mobile Malware Trends
The trends in the mobile malware world rely heavily on current global affairs. The main mode of transport for mobile malware is the type of applications that might be in demand. Hence, the latest shift in mobile malware trends came in 2020 with the global COVID-19 pandemic. The major shift in the daily lives of billions gave cybercriminals new opportunities to cast their malware net.
In 2020, mobile trojans still remained one of the biggest mobile security threats, and they were mostly hiding behind all sorts of software packages with the name “covid” in them. For example, a supposed Coronavirus Finder app tricked users into sharing their bank details because they supposedly had to pay a small fee for the service.
All in all, in 2020, more than 5.6 million malicious installation packages were detected, along with 156,710 new mobile banking Trojans and 20,708 new mobile ransomware Trojans. These types of mobile ransomware remain the most prominent threats. And while the number of attacks against mobile users experienced steady growth in 2020, looking at a broader perspective, we can see that the overall number remained more or less the same over the last few years.
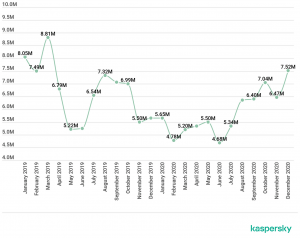
Mobile Malware Rates Chart – Source: Kaspersky
It does not mean, however, that the market for mobile malware is shrinking. As mentioned, mobile malware distribution is rather opportunistic, and it depends heavily on what is going on in the world. The drop of infections in the graph may correspond to a rather calm period in the global events.
Mobile Malware Mitigation
Ways to secure mobile devices are very similar to the methods employed by desktop users to avoid malware, too. One of the most important things is to use a secure Wi-Fi connection. If you have to transfer important data or access a sensitive data system, make sure that you are not connected to public Wi-Fi. It is better to use your data in such a case.
To avoid phishing scams and mobile Trojans, you should also be careful about the emails you receive. If it comes from someone you do not know, and it has an attached file or an outgoing link, there is a good chance that it could be a malware scam. Delete such an email immediately.
Downloading apps from reliable sources is of utmost importance, too. If some app is not available in your region, it is best to forfeit that program altogether instead of looking for third-party sources because third-party software packages could easily be exploited for mobile malware distribution.
It is also strongly recommended to avoid rooting your device. Rooting may give you more access to your device’s system, but it also opens the door for various malicious exploitations. Not to mention that you could lose your right to automatic security updates and vulnerability patches if you root your smartphone (or a tablet).
Although we do not offer mobile security products at the moment, we strongly recommend investing in a powerful anti-malware application that enhances your mobile device’s performance and makes sure that it stays protected against a number of malicious threats.
Last updated: 2026-02-07