Primary Malware Distribution Methods Extending to Mobile Apps and Social Media
 If we all knew exactly how, when and where malware would be distributed and avoided those instances, the world would be a better place nearly free from malicious software on most computers. Unfortunately, there is no such thing as a perfect world, and we have to live with the fact that hackers utilize many different methods for distributing malware to computers.
If we all knew exactly how, when and where malware would be distributed and avoided those instances, the world would be a better place nearly free from malicious software on most computers. Unfortunately, there is no such thing as a perfect world, and we have to live with the fact that hackers utilize many different methods for distributing malware to computers.
In the recently-released annual Human Factor 2016 report, the security firm Proofpoint revealed a few details that demonstrate how malware has evolved to be distributed on many different platforms, not just the expected email attachment. Email has proven to hold the title of the most popular method of distributing malware, but the latest trend for spreading malicious software falls on the platforms of mobile apps and social media.
A new age is upon us and mobile devices, mostly smartphones running either Android or iOS (iPhone), and social media are platforms that everyone uses in some capacity. If you aren't using a smartphone or a social media out, you're either a child or dead. The curiosity of human nature has also evolved, and hackers are eager to pounce on consumers of such technology with the latest and greatest malware threat.
Complicated methods for exploiting humanity have long gone and been replaced by the simpler things in life, social media and smartphones. Security researchers from Proofpoint have claimed that over two billion mobile apps infected with some form of data-stealing malware this year alone. Two billion! If every living human on this earth had a smartphone, that would be enough to infect the devices of about 35% of the world's population.
By ditching the pains in spend countless hours, days or months conjuring up complicated malware spreading methods; attackers have dumbed down their efforts. Because there are billions of people that utilize social networks and own smartphone devices, hackers have an upper hand with a platform foundation already laid that they can use to spread malware threats.
Malicious mobile apps are being spread through third party Android app stores as well as legitimate app stores where sneaky methods are used to host such programs. There have even been cases where malicious mobile apps were downloaded thousands of times from the Google Play app store, a place where you are supposedly safe for downloading apps. On social media, the number of phishing links is staggering, nearly ten times higher than links to download malicious mobile apps.
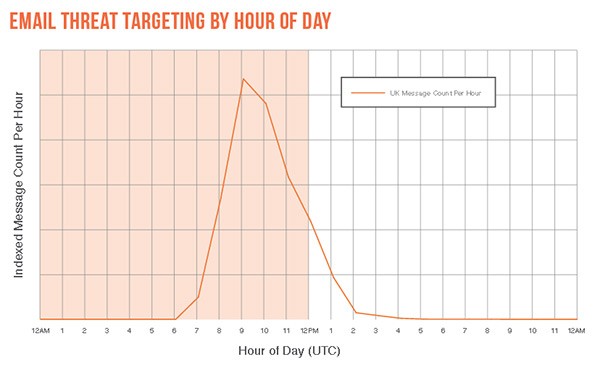
Probably one of the most interesting aspects of new malware distribution methods is the time of day that attackers are targeting computer users. In making sure malicious payloads are opened, hackers are timing their spam message campaigns to arrive on the victim's local time zone, around 9 am and 10 am. At such a time, computer users are more apt to opening up a spam email message as the work day begins and email inboxes are perused. Fundamentally, attackers are thinking smarter instead of working harder to exploit creative methods to spread malware.
The chart below is a clear representation of when spam email messages are sent and received during the day. The spike demonstrates the high message count per hour of emails tracked in the UK by Proofpoint.
Email threat targeting by hour of day chart – source: Proofpoint