Top 20 Countries Found to Have the Most Cybercrime

Have you ever wondered which countries face the most cybercrime? If you have ever wondered which countries have the most cybercrime, then you may be surprised to know that there are few contributing factors that attract cybercriminals to specific regions of the world. Security research firm, Symantec, has discovered specific factors that determine why a certain country is plagued with cybercrime more so or less than another which allowed them to come up with a ranking for each.
Symantec has ranked 20 countries that face, or cause, the most cybercrime. In compiling such a list, Symantec was able to quantify software code that interferes with a computer's normal functions, rank zombie systems, and observe the number of websites that host phishing sites, which are designed to trick computer users into disclosing personal data or banking account information. Symantec was also able to obtain data including the number of bot-infected systems which are those controlled by cybercriminals, rank countries where cyber attacks initiated and factor in the a higher rate of cybercrime in countries that have more access to broadband connections. The highest rate of cybercrime was found to be in the United States which may mainly contribute to the broad range of available broadband connections, which are those that allow uninterrupted internet connectivity.
All of the contributing factors allowed Symantec to effectively rank a top 20 list of countries that have the most cybercrime.
Table of Contents
List of Top 20 Countries with the highest rate of Cybercrime (source: BusinessWeek/Symantec)
Each country lists 6 contributing factors, share of malicious computer activity, malicious code rank, spam zombies rank, phishing website hosts rank, bot rank and attack origin, to substantiate its cybercrime ranking.
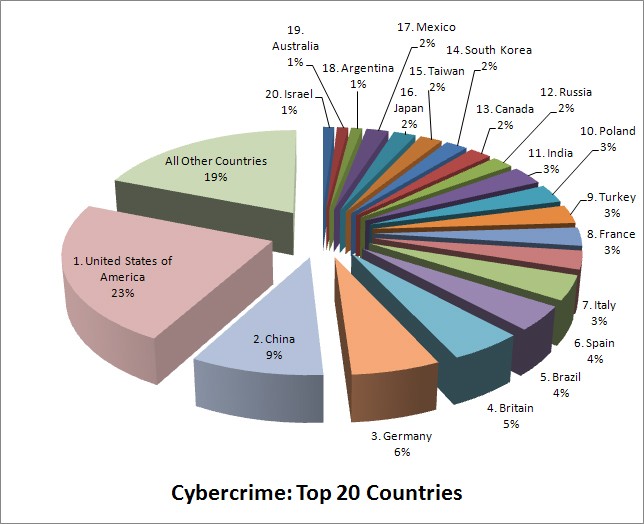
1. United States of America
Share of malicious computer activity: 23%
Malicious code rank: 1
Spam zombies rank: 3
Phishing web site hosts rank: 1
Bot rank: 2
Attack origin rank: 1
2. China
Share of malicious computer activity: 9%
Malicious code rank: 2
Spam zombies rank: 4
Phishing web site hosts rank: 6
Bot rank: 1
Attack origin rank: 2
3. Germany
Share of malicious computer activity: 6%
Malicious code rank: 12
Spam zombies rank: 2
Phishing web site hosts rank: 2
Bot rank: 4
Attack origin rank: 4
4. Britain
Share of malicious computer activity: 5%
Malicious code rank: 4
Spam zombies rank: 10
Phishing web site hosts rank: 5
Bot rank: 9
Attack origin rank: 3
5. Brazil
Share of malicious computer activity: 4%
Malicious code rank: 16
Spam zombies rank: 1
Phishing web site hosts rank: 16
Bot rank: 5
Attack origin rank: 9
6. Spain
Share of malicious computer activity: 4%
Malicious code rank: 10
Spam zombies rank: 8
Phishing web site hosts rank: 13
Bot rank: 3
Attack origin rank: 6
7. Italy
Share of malicious computer activity: 3%
Malicious code rank: 11
Spam zombies rank: 6
Phishing web site hosts rank: 14
Bot rank: 6
Attack origin rank: 8
8. France
Share of malicious computer activity: 3%
Malicious code rank: 8
Spam zombies rank: 14
Phishing web site hosts rank: 9
Bot rank: 10
Attack origin rank: 5
9. Turkey
Share of malicious computer activity: 3%
Malicious code rank: 15
Spam zombies rank: 5
Phishing web site hosts rank: 24
Bot rank: 8
Attack origin rank: 12
10. Poland
Share of malicious computer activity: 3%
Malicious code rank: 23
Spam zombies rank: 9
Phishing web site hosts rank: 8
Bot rank: 7
Attack origin rank: 17
11. India
Share of malicious computer activity: 3%
Malicious code rank: 3
Spam zombies rank: 11
Phishing web site hosts rank: 22
Bot rank: 20
Attack origin rank: 19
12. Russia
Share of malicious computer activity: 2%
Malicious code rank: 18
Spam zombies rank: 7
Phishing web site hosts rank: 7
Bot rank: 17
Attack origin rank: 14
13. Canada
Share of malicious computer activity: 2%
Malicious code rank: 5
Spam zombies rank: 40
Phishing web site hosts rank: 3
Bot rank: 14
Attack origin rank: 10
14. South Korea
Share of malicious computer activity: 2%
Malicious code rank: 21
Spam zombies rank: 19
Phishing web site hosts rank: 4
Bot rank: 15
Attack origin rank: 7
15. Taiwan
Share of malicious computer activity: 2%
Malicious code rank: 11
Spam zombies rank: 21
Phishing web site hosts rank: 12
Bot rank: 11
Attack origin rank: 15
16. Japan
Share of malicious computer activity: 2%
Malicious code rank: 7
Spam zombies rank: 29
Phishing web site hosts rank: 11
Bot rank: 22
Attack origin rank: 11
17. Mexico
Share of malicious computer activity: 2%
Malicious code rank: 6
Spam zombies rank: 18
Phishing web site hosts rank: 31
Bot rank: 21
Attack origin rank: 16
18. Argentina
Share of malicious computer activity: 1%
Malicious code rank: 44
Spam zombies rank: 12
Phishing web site hosts rank: 20
Bot rank: 12
Attack origin rank: 18
19. Australia
Share of malicious computer activity: 1%
Malicious code rank: 14
Spam zombies rank: 37
Phishing web site hosts rank: 17
Bot rank: 27
Attack origin rank: 13
20. Israel
Share of malicious computer activity: 1%
Malicious code rank: 40
Spam zombies rank: 16
Phishing web site hosts rank: 15
Bot rank: 16
Attack origin rank: 22
Cybercrime is expected to impose damage of up to $10.5 trillion annually by 2025
According to a research report by Cybersecurity Ventures, the global costs of cybercrime activity may increase by 15 percent annually over the next five years, reaching an estimated damage of $10.5 trillion annually by 2025. For comparison, the same number was $3 trillion in 2015. This massive transfer of economic wealth undermines innovation and investment, as it is larger than the cost inflicted by natural disasters. Moreover, it brings profits to the entities that engage in it higher than the profits achieved by trading all major illegal drugs combined. Stolen funds, loss of intellectual property and other valuable data, drop in productivity, identity theft, and reputational harm are some of the heaviest consequences of a severe hacking attack suffered by individual PC users and businesses.
Spending on cybersecurity products and services will surge to $1.75 trillion from 2021-2025
All the risks associated with hacking attacks put digitized businesses under enormous pressure to find a way to secure their data, customers, networks, and Internet of Things (IoT) devices from cybercrime. Spending on cybersecurity products and services is supposed to reach a total of $1.75 trillion globally for the five years from 2021 to 2025, turning that market into one of the fastest-growing sectors of the IT economy. One particular high-damage sector is Ransomware, where the predicted costs may exceed $265 billion annually by 2031, which reflects a 57X increase to $20 billion for six years. Cybersecurity ventures have also estimated that Ransomware is the fastest-growing malware type that will hit a business every few seconds this year. That frequency is likely to increase to every two seconds by 2031. Considering the rapid growth of global data storage on public clouds operated by social media platforms, private vendors, and clouds owned by governments and institutions, the amount of data that will need to be protected may surpass 200 zettabytes by 2025.
The Ransomware market is growing exponentially
Authorities worldwide have managed to bust several significant Ransomware gangs this year, yet that particular malware type is very far from being extinguished. New, highly sophisticated threats emerge to take the place of the older ones while the attacks get more effective and lucrative.
Cybersecurity experts expect hacking gangs will continue to refine and intensify their activities, always one step ahead of businesses struggling to secure their defenses with a broad range of protection tools and corporate risk priorities. The latest research on ransomware extortion mechanisms and infection vectors also points out that human-generated risk continues to dominate the propagation means of this malware threat. Indeed, the human element allowed 82 percent of ransomware attacks in 2021, with 25% of analyzed breaches resulting from social engineering attacks, as stated in the Verizon Data Breach Investigations Report (DBIR) for 2022. The statistics thus raise another point - training programs focused on cybersecurity awareness and education should become an inevitable part of all corporate training and campaigns.
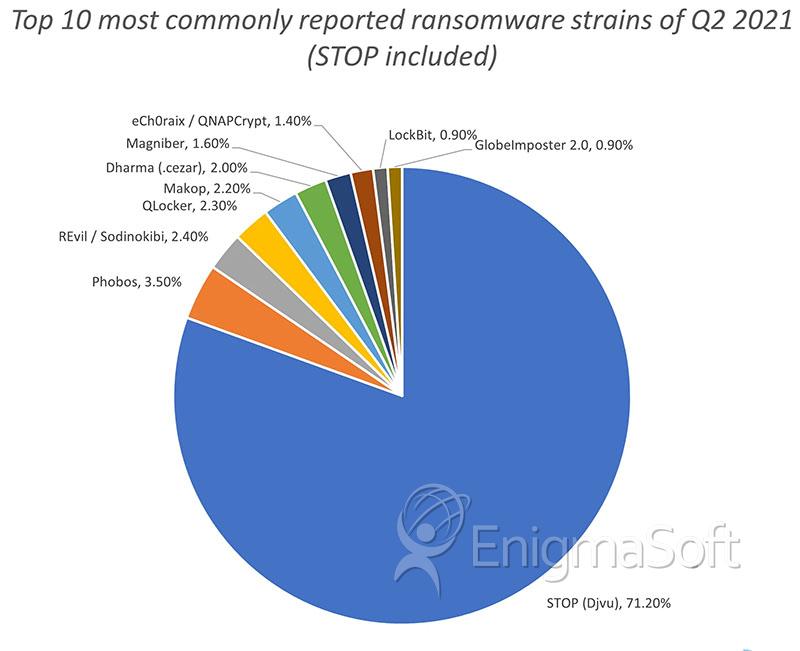
The following chart from Emsisoft.com depicts the most common strains of ransomware detected in the second quarter of 2021.
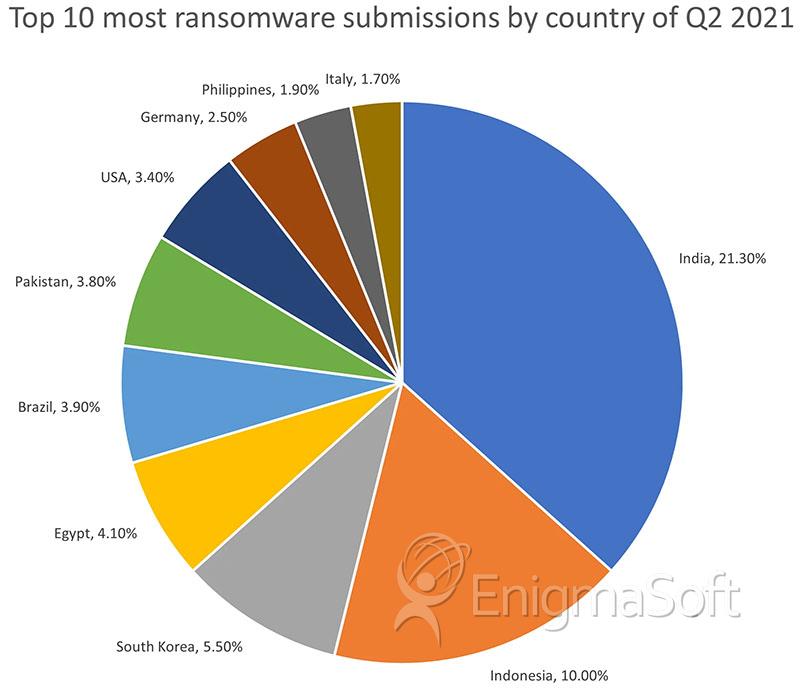
Countrywide, the following Emsisoft.com chart shows the 10 countries that made up 58.10% of all global ransomware submissions for the second quarter of 2021.
Latest Cybersecurity Trends
Several trends have been observed to rule the business in recent years. One of the most popular ways to protect devices and networks from malware is multi-factor authentication (MFA). An even more secure method used by many companies is combining MFA with passwords, which adds another layer of protection and reduces data leak risks. MFA means that users need to verify their identity on two or more devices, and it is probably the most effective and applicable means of preventing unauthorized access to third-party applications or malicious other malicious actors. Another notable trend is the enhanced use of smart devices that fall into the Internet of Things (IoT) category. Malware threats targeting cloud products and services are another aspect that should be followed closely. Companies using cloud services for data storage and corporate communication will look for effective and accessible cybersecurity solutions. Increased use of artificial intelligence applications and other automated systems may also lead to higher risks of unexpected malware attacks.