Are You Sure You’re NOT Infected with Malware?
Don’t Fall Victim to Malware or Ransomware Attacks!
Detect and remove malware, viruses, ransomware & other threats for FREE! Get Protected with SpyHunter.
Download SpyHunter (FREE Trial!)*A keylogger is a software or a hardware tool that is used for keystroke logging. This practice refers to an action when every single key struck on a keyboard is recorded in secret. Usually, the person being monitored is not aware of it. A keylogger logs all the keystrokes in a file, and then it can upload this file to a predestined server.
There are many types of keyloggers out there, and they can be used for different purposes. Although initially, keylogger was not supposed to be a cybercrime tool, it did not take long for cybercriminals to apply keylogging in their daily activities, too.
Software vs. Hardware
The complexity of describing a keylogger lies in the fact that there are multiple types of keyloggers out there, and they could be classified based on several different variables. The most common classification is based on design. As such, there are software-based and hardware-based keyloggers.
Software keyloggers essentially are programs that get installed on a target computer. Depending on the classification, these applications may be further divided into programs that make use of a hooking mechanism and kernel or driver-based keyloggers.
The former will usually enter the computer as an executable file that launches the hook function. It is a legitimate Windows function else known as SetWindowsHookEx, and it is used to monitor your system for specific types of events. In order words, if a third-party application makes use of this system messaging mechanism, it can monitor your system and process the messages sent before they actually reach the appropriate target procedure. The difference between the hooking function-based and the kernel-based keyloggers is that the latter have the root access, and they can be virtually undetectable. In a sense, kernel-based keyloggers can be considered rootkits that can acquire illegal access to the hardware.
Hardware keyloggers, on the other hand, do not depend on any program or application to function because they work at a hardware level. That would be a specific device that records all the communication between your computer and your keyboard. Regular hardware keyloggers are placed somewhere in between the keyboard and computer, while there are also such hardware keylogger types as wireless keylogger sniffers, firmware, and keyboard overlays.
Legal vs. Illegal
Those who deal with malware on a daily basis are used to the malicious description of a keylogger, but the term itself is not malicious. It is only a program that is supposed to monitor someone’s activity. Therefore, there are both legal and illegal aspects of this software.
Legal keylogging programs might be used by employers to track the online activities of their employees in order to make sure that they do their job properly. Also, computer users may track their system activity via such programs in case their computers are used by third parties. What’s more, a keylogger may be a tool of parental control, enabling parents to track their children’s Internet activity. For the most part, these programs are supposed to ensure security in one way or the other. However, the thin ethical line between safety monitoring and downright spying makes keylogging a delicate subject.
The illegal use of keyloggers involves various types of cybercrimes. It can be used as a part of a trojan or a rootkit for data collection. Seeing how a keylogger can record all the keyboard input data, cybercriminals can intercept PIN codes, passwords, logins, email addresses, and other sensitive information without any difficulty. Such practice is highly dangerous both on the individual and corporate level, and that is why computer security experts advise users to perform regular system scans with security applications.
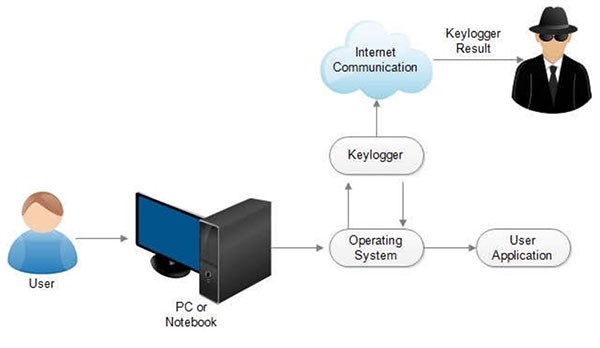
Keylogger Processes – Source: Researchgate.net
There are many malicious infections that employ keyloggers, but to name just a few, perhaps we could start with the Predator Pain Keylogger that includes Browser, File, FTP, and Messenger stealers in its setup. This keylogger usually attacks online gamers, stealing passwords and usernames from Minecraft, Steam, and World of Warcraft users. According to extensive research, the program is usually distributed via infected USB flash drives or P2P websites.
A far more common type of infection that uses keylogging is a trojan. In this case, we could mention the Haxdoor Trojan. This malicious banking trojan appeared in 2006, and it was distributed via spam email messages that looked like legitimate notifications from a bank. This backdoor trojan with rootkit capabilities would collect banking usernames, passwords, credit card information, login details, and other financial information. With this data, the people behind this infection could steal millions of dollars from unsuspecting users.
Another good example of a trojan that employed keylogging is the notorious Zeus Trojan or Trojan.Zbot that was first discovered in 2010. The goal of this infection is to steal confidential information from the affected computer. Zeus Trojan usually spreads around via spam tools and drive-by downloads. Email messages that distribute this infection usually look like they have been sent from MySpace, Microsoft, Facebook, or any other reliable platform. Users are urged to click a link in the message, and once they do that, they get infected with the trojan. According to various security reports, the Zeus Trojan usually targets banking information, but it can be easily customized to steal other data as well.
Aside from the cases when keyloggers are installed legally for company security, parental control, or other justifiable purposes, the malicious infections with the keylogging function spread just like any other malware program out there. The distribution methods can be mainly grouped into four categories:
In the case of spam email, users get infected with keyloggers when they open the file attached to the message or click the embedded link. Browser vulnerability exploit refers to a method of malware distribution when the program download is launched automatically once the user visits the infected page. By “malicious program” in the third distribution method, we mean a situation when a keylogger is downloaded to your system by a malicious application that has already been running on your PC. Usually, trojans are able to connect to the Internet behind your back and download more unwanted programs. Finally, a keylogger may also enter your computer when you open its installer file on a P2P network. With this, we can see that when it comes to avoiding this type of threat, a lot depends on the users themselves.
The most efficient way to protect yourself from this and other types of infections is by installing a licensed anti-malware application. If your computer security tool is up-to-date, it will have all of the currently detected keyloggers in its definition database, and it will be able to intercept them immediately.
Users should also consider using one-time passwords, two-factor authentication, and virtual keyboards when they need to enter sensitive data. You should especially consider it when you use a third-party or a public computer. When it comes to keyloggers, it is not so much your computer that you should be worried about, but your personal information!
| # | Threat Name |
Severity Level
Severity Level: The determined severity level of an object, represented
numerically, based on our risk modeling process and research, as explained in our
Threat Assessment Criteria.
|
Alias(es) |
Detections
Detections: The number of confirmed and suspected cases of a particular threat detected on
infected computers as reported by SpyHunter.
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Keylogger.Refog | 80 % (High) | 1,209 | |
| 2. | HomeKeyLogger | 80 % (High) | 822 | |
| 3. | Keylogger.TTiger | 80 % (High) | 11 | |
| 4. | SaveKeys | 80 % (High) | 2 | |
| 5. | Trojan.Spy.KeyLogger.MA | |||
| 6. | Force Keylogger | |||
| 7. | Windows Keylogger | 80 % (High) | 675 | |
| 8. | Guardian Monitor | 100 % (High) |
Suspicious file Guardian Monitor Spyware.GuardMon |
|
| 9. | Trojan.MSIL.Keylogger | 80 % (High) | 650 | |
| 10. | StealthWatcher | 80 % (High) | 4 | |
| 11. | Ispy | 80 % (High) | ||
| 12. | MonitoringTool.XPCSpyPro | 80 % (High) | 4 | |
| 13. | Trojan.Spy.KeyLogger.U | |||
| 14. | Keylogger.MSIL.Keylogger.DH | 80 % (High) | ||
| 15. | Keylogger.MSIL.SnakeLogger.DO | 80 % (High) | 24 | |
| 16. | Invisible Keylogger 97 | 80 % (High) | 14 | |
| 17. | StarLogger | 80 % (High) | 4 | |
| 18. | HeurEngine.Packed-MaskPE | |||
| 19. | Keylogger.MSIL.SnakeLogger.DL | 80 % (High) | 682 | |
| 20. | SnapKey | 80 % (High) | 4 | |
| 21. | Keylogger.WebsiteSpyMonitor | 80 % (High) | ||
| 22. | 'Taxve Inc.' Email Virus | |||
| 23. | PrintMonitor | 80 % (High) | 35 | |
| 24. | Spector | 80 % (High) | 711 | |
| 25. | Keylogger.PredatorPain | 80 % (High) | 375 | |
| 26. | Keylogger.HiddenCamera.d | 80 % (High) | ||
| 27. | KeyKey (keylogger) | 80 % (High) | 75 | |
| 28. | Trojan.Keylogger.K | 80 % (High) | 202 | |
| 29. | Keylogger.Refog.A | 80 % (High) | 166 | |
| 30. | Nova Keylogger |
Last updated: 2026-02-07
| Threat Name |
Severity Level
Severity Level: The determined severity level of an object, represented
numerically, based on our risk modeling process and research, as explained in our
Threat Assessment Criteria.
|
Detections
Detections: The number of confirmed and suspected cases of a particular threat detected on
infected computers as reported by SpyHunter.
|
|---|---|---|
| 'Taxve Inc.' Email Virus | ||
| 123Keylogger | 80 % (High) | 4 |
| 404 Keylogger | ||
| AceSpy | 60 % (Medium) | 0 |
| Achtung! | 80 % (High) | 12 |
| Actions Monitor | 80 % (High) | 50 |
| Activity Monitor | 80 % (High) | 85 |
| Actual Spy | ||
| ACXInstall | 70 % (High) | 2 |
| AGM65s Keylog trojan | ||
| All In One Keylogger | 80 % (High) | 3 |
| Aobo Keylogger | ||
| Application.Actual_Keylogger | 80 % (High) | 6,029 |
| Application.Family_Keylogger | 80 % (High) | 1 |
| Application.WinSpy_Stealth_Monitor | ||
| Application.WinSpy_Stealth_Monitor Virus | ||
| Ardamax Keylogger | 80 % (High) | 0 |
| Atomic Log | 80 % (High) | 15 |
| Black Box AOL Logger | 80 % (High) | 13 |
| BlazingTools Perfect Keylogger | 80 % (High) | 14 |
| Boolosoft Keylogger | 80 % (High) | 0 |
| CheaterChecker | 10 % (Normal) | 2,259 |
| Cyber Snoop | ||
| DesktopSnooper | 80 % (High) | 1 |
| Enfiltrator Black Box | 50 % (Medium) | 0 |